文章目录
1、背景
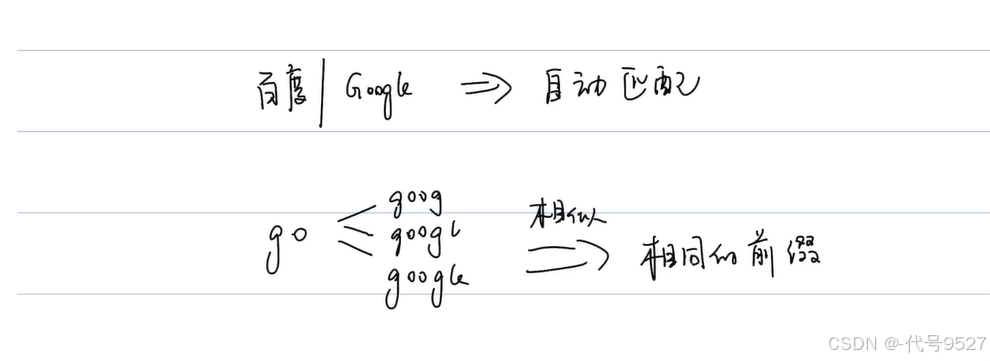
如上,以浏览器搜索时的自动匹配为例:

如果把所有搜索关键字放一个数组里,则:插入、搜索一个词条时,时间复杂度为O(n),判断某个前缀是否存在,时间复杂度为O(n × m),m为词条长度,因为在遍历数组时,要挨个对比数组每个元素的每个字符和词条前缀的每个字符是否相同,得两层for循环,时间复杂度太高,比如在以下数组判断是否有前缀为haha的关键字:
[goog,googl,google,bai,baidu,gi] 2、前缀树Trie
前缀树,又叫字典树,是一种数据结构,Trie,发音类似 “try”。比如存以下这些数据到前缀树:
goog,googl,google,bai,baidu,gi 效果:
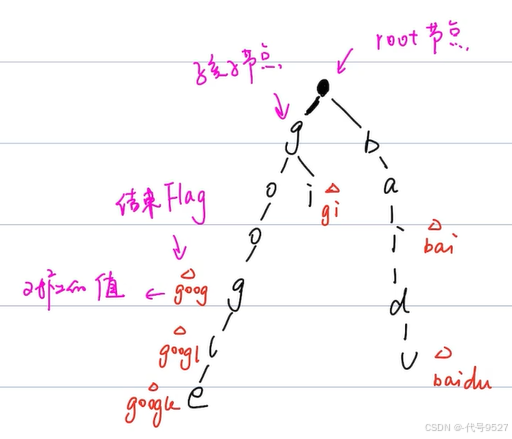
root节点,一般不存数据,其下有孩子节点。以goog为例,存到第二个g时,这个单词没了,此时,这儿所在的节点,会有一个结束的Flag,以及该Flag处对应的值。从以上的分析,大致可以看出,前缀树Trie这种结构,其对象应该有以下属性:
- 孩子节点children
- 某个单词的结束标志isEnd
关于时间复杂度,如果输入字符串str,其长度为k:
- 插入:O(k)
- 搜索:O(k)
- 判断是否存在str这个前缀的词语:O(k)
关于前缀树这种结构的应用场景:
- 前缀匹配
- 词频统计(做统计,当然也可用HashMap实现)
3、leetcode208:实现Trie
以英语单词为例,26个字母,根据ASCII码转为数字,就是数组的下标。Trie类应该有个isEnd属性,因为要区分:
- 是否有str这个单词
- 是否有以str开头(为前缀)的单词
比较到str的最后一个字母,isEnd为true,说明有str这个单词,是否有这个前缀,则不用考虑isEnd。
此外,正常来说,每个Trie节点的值val也要存一下,但对英文字母不用,因为其对应的SSCII码,可以当下标,下标转一下就是字母值。
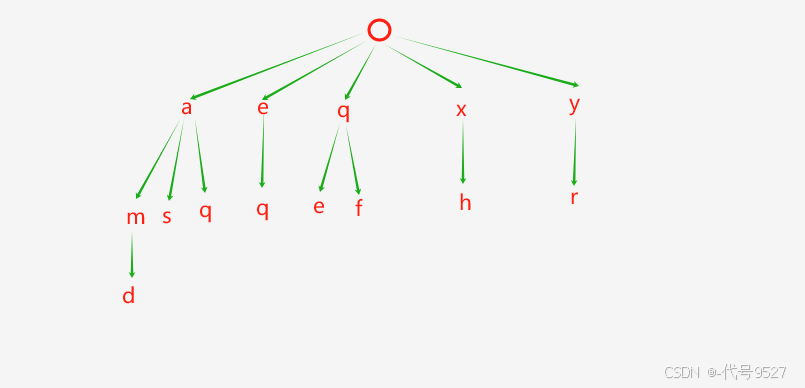
参照以上示意图,每个节点上存着一个字母(索引与ASCII码),写前缀树的实现:
public class Trie { private Trie[] children; private boolean isEnd; public Trie() { // 26个英文字母,每个节点最多26个儿子节点 children = new Trie[26]; isEnd = false; } public void insert(String word) { // 调用insert方法的对象,可认为是根节点 Trie node = this; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); // 字母转ASCII码,a对应97,减去a,可让值从0开始,而不是97,方便对应数组下标 int index = ch - 'a'; if (node.children[index] == null) { // 这是个新字母,创建一个新的节点,作为子节点 // 这个节点对应的字母的值不用存,下标+97转回去就是这个节点的值 node.children[index] = new Trie(); } // 该判断word里的下一个字母了,node节点不再是根节点,而是第一个字母的对应的节点 node = node.children[index]; } // 整个word都遍历完了,结束标志为置为true node.isEnd = true; } public boolean search(String word) { Trie node = this; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); // 字母转ASCII码,a对应97,减去a,可让值从0开始,而不是97,方便对应数组下标 int index = ch - 'a'; if (node.children[index] == null) { // 往下顺,如果有字母不一样,说明一定不存在这个单词 return false; } // 检查下一个字母,替换下Tire节点 node = node.children[index]; } // 和判断前缀是否存在不一样,搜索,找到末尾后,末尾这儿必须有单词的结束标志isEnd return node.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { Trie node = this; for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) { char ch = prefix.charAt(i); // 字母转ASCII码,a对应97,减去a,可让值从0开始,而不是97,方便对应数组下标 int index = ch - 'a'; if (node.children[index] == null) { return false; } // 检查下一个字母,替换下Tire节点 node = node.children[index]; } return true; } } 搜索和判断前缀的代码重复度太高,优化下,抽取公共代码
public class Trie { private Trie[] children; private boolean isEnd; public Trie() { // 26个英文字母,每个节点最多26个儿子节点 children = new Trie[26]; isEnd = false; } public void insert(String word) { // 调用insert方法的对象,可认为是根节点 Trie node = this; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); // 字母转ASCII码,a对应97,减去a,可让值从0开始,而不是97,方便对应数组下标 int index = ch - 'a'; if (node.children[index] == null) { // 这是个新字母,创建一个新的节点,作为子节点 // 这个节点对应的字母的值不用存,下标+97转回去就是这个节点的值 node.children[index] = new Trie(); } // 该判断word里的下一个字母了,node节点不再是根节点,而是第一个字母的对应的节点 node = node.children[index]; } // 整个word都遍历完了,结束标志为置为true node.isEnd = true; } /** * 搜索和判断前缀是否存在,两个操作的公共逻辑抽取 * * @param str 输入的字符串 * @return 返回最后一个字母对应的Trie节点,无则返回null */ public Trie getTrieNode(String str) { if (str == null) { return null; } // 调用insert方法的对象,可认为是根节点 Trie node = this; for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { char ch = str.charAt(i); // 字母转ASCII码,a对应97,减去a,可让值从0开始,而不是97,方便对应数组下标 int index = ch - 'a'; if (node.children[index] == null) { // 往下顺,如果有字母不一样,说明一定不存在这个单词或前缀 return null; } // 检查str的下一个字母,替换下Tire节点 node = node.children[index]; } return node; } public boolean search(String word) { Trie trieNode = getTrieNode(word); // 和判断前缀是否存在不一样,搜索,找到末尾后,末尾这儿必须有单词的结束标志isEnd return trieNode != null && trieNode.isEnd; } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { return getTrieNode(prefix) != null; } } 从优化后的代码可以看到,搜索和判断前缀的区别是,判断到输入字符的最后一个字母后,搜索要有isEnd标志为true,表示有这样的单词,以免出现,搜abc,但只有abcd时也返回true的情况。而判断前缀是否存在,则不用考虑这个标志位。
4、leetcode720:词典中最长的单词

如题中示例1,能返回world,需要前面有w ⇒ wo ⇒ wor ⇒ worl这四个词语才行
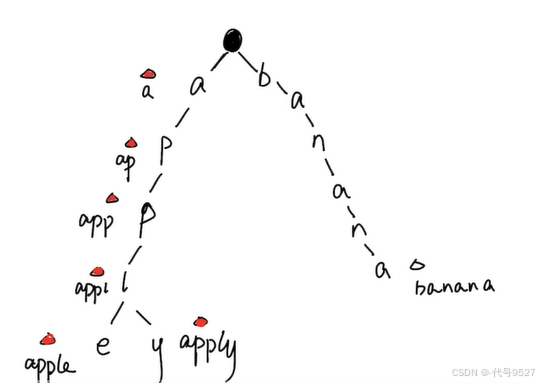
将题中数组的每个单词存入前缀树,然后遍历数组。比如app单词,a字母找到了,且isEnd为true,往下ap,也找到了,且isEnd为true,如此app这个单词就是目前符合要求的。
public class P720 { public String longestWord(String[] words) { if (null == words || words.length == 0) { return ""; } Trie trie = new Trie(); for (String word : words) { trie.insert(word); } String result = ""; // 控制精确跳到外层循环,而不是内层 outerLoop: for (String word : words) { String temp = ""; for (String s : word.split("")) { temp = temp + s; if (!trie.search(temp)) { // 如果有一个字母找不到,则直接看题中数组里的下一个单词 continue outerLoop; } } // 判断完一个单词符号要求后,如果长度超过了result,则替换 if (word.length() > result.length()) { result = word; } else if (word.length() == result.length()) { // 如果判断完一个单词符号要求后,如果长度等于result,则对比,取字典序小的 // compareToIgnoreCase() 方法与 compareTo() 方法类似,但会忽略大小写 result = word.compareToIgnoreCase(result) < 0 ? word : result; } } return result; } } 以上,套用了208题的Trie类的search方法,search方法只判断搜到末尾时,isEnd是否为true,即它只关心有没有world这个词,而不关心有没有w ⇒ wo ⇒ wor ⇒ worl这四个词语(isEnd为true),再修改下search方法:
public class Trie { private Trie[] children; private boolean isEnd; //略,同上一题 /** * 搜索是否有word单词,以及w ⇒ wo ⇒ wor ⇒ worl这四个单词 */ public boolean searchByStep(String word) { if (word == null) { return false; } // 根节点 Trie node = this; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); int index = ch - 'a'; // 没有这个字母,或者这地方结束标志为false,则返回false if (node.children[index] == null || !node.children[index].isEnd) { return false; } // 检查str的下一个字母,替换下Tire节点 node = node.children[index]; } // 到最后一个字母所在的节点了 return node != null && node.isEnd; } } 用新的前缀树搜索方法(判断word是否存在的同时,还要判断w ⇒ wo ⇒ wor ⇒ worl这四个是否存在),并简化下实现代码:
public class P720 { public String longestWord(String[] words) { if (null == words || words.length == 0) { return ""; } Trie trie = new Trie(); for (String word : words) { trie.insert(word); } String result = ""; for (String word : words) { // 不符合条件,判断下一个单词 if (!trie.searchByStep(word)) { continue; } // 判断完一个单词符合要求后,如果长度超过了result,则替换 // 如果判断完一个单词符号要求后,如果长度等于result,则对比,取字典序小的替换result // compareToIgnoreCase() 方法与 compareTo() 方法类似,但会忽略大小写 if (word.length() > result.length() || (word.length() == result.length()) && word.compareToIgnoreCase(result) < 0) { result = word; } } return result; } } 