文章目录
前置知识 @SentinelResource的实现原理、SphU.entry()方法中ProcessorSlotChain链、entry.exit()
建议先会使用sentinel,并对底层实现有一些理解再来看sentinel规则持久化。当然你直接看也能看懂。
Sentinel规则的推送有下面三种模式:
| 推送模式 | 说明 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原始模式 | API 将规则推送至客户端并直接更新到内存中,扩展写数据源 WritableDataSource | 简单,无任何依赖 | 不保证一致性;规则保存 在内存中,重启即消失。 严重不建议用于生产环境 |
| Pull模式 | 客户端主 动向某个规则管理中心定期轮询拉取规 则,这个规则中心可以是 DB、文件等。扩展写数据源 WritableDataSource | 简单,无任何依赖; 规则持久化 | 不保证一致性;实时性不 保证,拉取过于频繁也可 能会有性能问题。 |
| Push模式 | 规则中心 统一推送,客户端通过注册监听器的方 式时刻监听变化,比如使用 Nacos、 Zookeeper 等配置中心。这种方式有 更好的实时性和一致性保证。生产环境 下一般采用 push 模式的数据源。扩展读数据源 ReadableDataSource | 规则持久化;一致 性;快速 | 引入第三方依赖 |
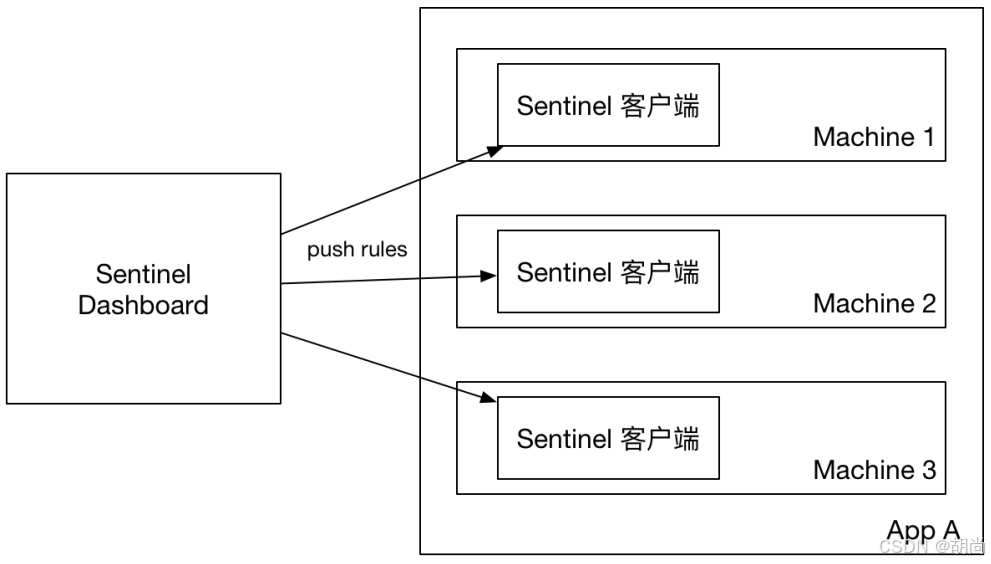
原始方式
如果不做任何修改,Dashboard 的推送规则方式是通过 API 将规则推送至客户端 并直接更新到内存中:
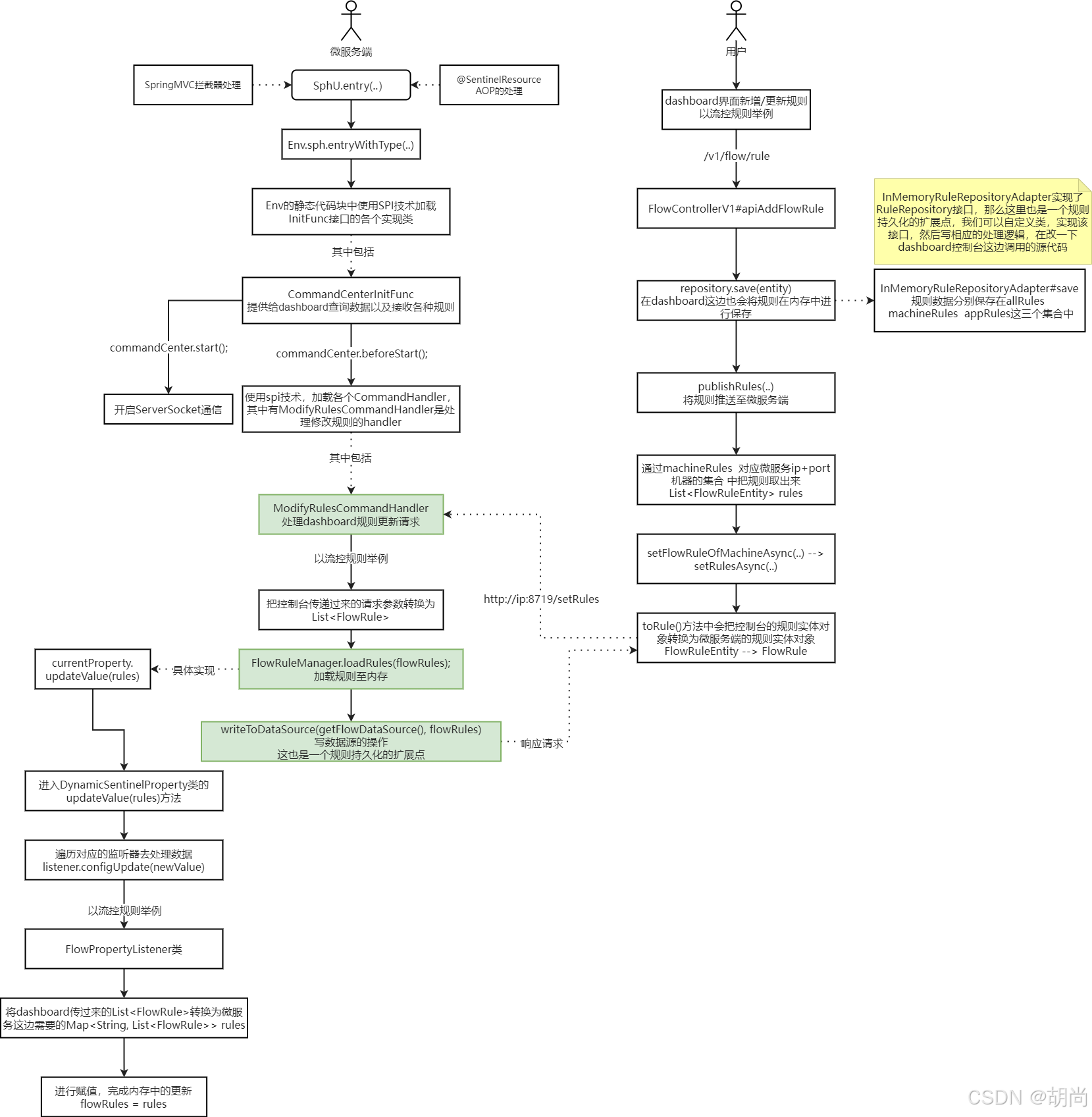
微服务端规则如何保存
我们先来看看我们微服务这边规则是如何保存的。就以流控为例
在FlowSlot类的entry()方法中,它会先取出当前资源所有流控规则
// 取当前资源所有流控规则 Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName()); if (rules != null) { for (FlowRule rule : rules) { // 校验流控 if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) { throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule); } } } // 继续更近ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName())方法,进入到FlowSlot.apply() public Collection<FlowRule> apply(String resource) { // 缓存规则 Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap(); return flowRules.get(resource); } // 我们知道了是通过FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap();这个流控规则管理器得到了流控规则集合。继续更近该方法 public class FlowRuleManager { // 找到了真正保存内存中规则对象的map private static volatile Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = new HashMap<>(); 。。。 } 我们现在就知道了下面这些数据:
微服务端 规则实体对象:
FlowRule微服务端 缓存流控规则管理器:
FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap()微服务端 保存规则的集合定义
Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = new HashMap<>()微服务端 加载规则进内存
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
规则如何加载进内存
sentinel的入门代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) { // 配置规则. initFlowRules(); while (true) { // 1.5.0 版本开始可以直接利用 try-with-resources 特性 try (Entry entry = SphU.entry("HelloWorld")) { // 被保护的逻辑 System.out.println("hello world"); } catch (BlockException ex) { // 处理被流控的逻辑 System.out.println("blocked!"); } } } private static void initFlowRules(){ List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>(); FlowRule rule = new FlowRule(); rule.setResource("HelloWorld"); rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); // Set limit QPS to 20. rule.setCount(20); rules.add(rule); // 核心代码,加载规则进内存 // 可以发现 这里也是使用的流控规则管理器FlowRuleManager FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); } 真正将规则加载进内存中FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);:
- 遍历PropertyListener监听器集合,找对应的监听器去处理
- 将传过来的list转换为我们对应的Map集合
Map<String, List<FlowRule>> rules - 直接复制给flowRules这个成员属性,这里就和上面微服务端规则如何保存串联起来了
public static void loadRules(List<FlowRule> rules) { // 加载资源进内存 Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules 集合中 currentProperty.updateValue(rules); } // 调用进DynamicSentinelProperty#updateValue方法中 public boolean updateValue(T newValue) { if (isEqual(value, newValue)) { return false; } RecordLog.info("[DynamicSentinelProperty] Config will be updated to: {}", newValue); value = newValue; for (PropertyListener<T> listener : listeners) { // 对应的监听器去处理 listener.configUpdate(newValue); } return true; } // 这里会调用进FlowRuleManager的内部类FlowPropertyListener.configUpdate() public synchronized void configUpdate(List<FlowRule> value) { // 将传过来的list转换为我们对应的Map集合 Map<String, List<FlowRule>> rules = FlowRuleUtil.buildFlowRuleMap(value); if (rules != null) { // 直接复制给flowRules这个成员属性 // 这里就和上面微服务端规则如何保存串联起来了 flowRules = rules; } RecordLog.info("[FlowRuleManager] Flow rules received: {}", rules); } 微服务端接收控制台请求
我们知道我们使用sentinel和springcloudAlibaba整合会调用
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel依赖,而在这个依赖中的spring.factories文件中会定义一个SentinelWebAutoConfiguration自动配置类,它实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口,并重写addInterceptors()方法它会添加拦截器,拦截器中会对我们的请求进行拦截并添加定义资源的代码Entry entry = SphU.entry(...)我们直接使用
@SentinelResource注解方式,spring.factories文件中会定义一个SentinelAutoConfiguration自动配置类,并添加了一个SentinelResourceAspectBean对象,它通过AOP对要执行的目标方法也加了定义资源的代码Entry entry = SphU.entry(...)
而在Env类的静态代码块中,会使用SPI加载InitFunc接口,加载出来的其中一个核心类,客户端启动的接口服务,提供给dashboard查询数据以及接收各种规则使用:com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.init.CommandCenterInitFunc :
- 使用spi技术,加载各个CommandHandler,其中有ModifyRulesCommandHandler是处理修改规则的handler
- 开启ServerSocket通信
public class CommandCenterInitFunc implements InitFunc { @Override public void init() throws Exception { CommandCenter commandCenter = CommandCenterProvider.getCommandCenter(); if (commandCenter == null) { RecordLog.warn("[CommandCenterInitFunc] Cannot resolve CommandCenter"); return; } // 使用spi技术,加载各个CommandHandler,其中有ModifyRulesCommandHandler是处理修改规则的handler commandCenter.beforeStart(); // 开启ServerSocket通信 commandCenter.start(); RecordLog.info(...); } } 进入ModifyRulesCommandHandler类的handler()方法:
- 把控制台传递过来的请求参数转换为
List<FlowRule> - 加载规则,直接调用FlowRuleManager流控规则管理器的loadRules()方法
- 写数据源的操作,默认情况下是没有WritableDataSource,我们可以在这里进行扩展进行持久化操作
- 响应给sentinel控制台
// 注意name = "setRules",这就是控制台请求服务端的url路径 @CommandMapping(name = "setRules", desc = "modify the rules, accept param: type={ruleType}&data={ruleJson}") public class ModifyRulesCommandHandler implements CommandHandler<String> { public CommandResponse<String> handle(CommandRequest request) { //...... // 处理流控规则 if (FLOW_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) { // 把控制台传递过来的请求参数转换为 List<FlowRule> List<FlowRule> flowRules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, FlowRule.class); // 加载规则,直接调用FlowRuleManager流控规则管理器的loadRules()方法 // 这里就和上方 微服务端规则是如何加载进内存的串联起来了 FlowRuleManager.loadRules(flowRules); // 关键一步,这里会有一个写数据源的操作。默认情况下是没有WritableDataSource,我们可以在这里进行扩展 if (!writeToDataSource(getFlowDataSource(), flowRules)) { result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG; } // 响应给sentinel控制台 return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result); // 处理权限规则 } else if (AUTHORITY_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) { List<AuthorityRule> rules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, AuthorityRule.class); AuthorityRuleManager.loadRules(rules); if (!writeToDataSource(getAuthorityDataSource(), rules)) { result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG; } return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result); // 处理熔断规则 } else if (DEGRADE_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) { List<DegradeRule> rules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, DegradeRule.class); DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules); if (!writeToDataSource(getDegradeDataSource(), rules)) { result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG; } return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result); // 处理系统规则 } else if (SYSTEM_RULE_TYPE.equalsIgnoreCase(type)) { List<SystemRule> rules = JSONArray.parseArray(data, SystemRule.class); SystemRuleManager.loadRules(rules); if (!writeToDataSource(getSystemSource(), rules)) { result = WRITE_DS_FAILURE_MSG; } return CommandResponse.ofSuccess(result); } return CommandResponse.ofFailure(new IllegalArgumentException("invalid type")); } } 控制台推送规则
我们在sentinel控制台进行了资源规则的更新,控制台是如何通知微服务进行相应的更新操作的嘞?
dashboard控制台处理web界面请求的位置是FlowControllerV1,请求路径为/v1/flow/rule,新增规则是POST请求,修改规则是PUT规则
- 在dashboard这边也会将规则在内存中保存一份
- 调用微服务端,更新规则
// 不管是新增规则还是更新规则,处理细枝末节的代码,关键代码就是下面这两行 public Result<FlowRuleEntity> apiAddFlowRule(@RequestBody FlowRuleEntity entity) { ...... try { // 在dashboard这边也会将规则在内存中进行保存 entity = repository.save(entity); // 调用微服务端,更新规则 publishRules(entity.getApp(), entity.getIp(), entity.getPort()).get(5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); return Result.ofSuccess(entity); } catch (Throwable t) { ...... } } 首先看dashboard这边是如何将规则在内存中保存的,这里会调用到InMemoryRuleRepositoryAdapter#save,从这个类名就能看出来是操作内存的
这个类实现了RuleRepository接口,那么这里也是一个规则持久化的扩展点,我们可以自定义类,实现该接口,然后写相应的处理逻辑,在改一下dashboard控制台这边调用的源代码。(这种方式可以先考虑,但不是必须要这么做)
- 将规则数据分别保存在allRules machineRules appRules这三个集合中
public T save(T entity) { if (entity.getId() == null) { entity.setId(nextId()); } T processedEntity = preProcess(entity); if (processedEntity != null) { // 所有规则集合中保存一份 allRules.put(processedEntity.getId(), processedEntity); // 对应微服务ip+port机器的集合中保存一份 machineRules.computeIfAbsent(MachineInfo.of(processedEntity.getApp(), processedEntity.getIp(), processedEntity.getPort()), e -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>(32)) .put(processedEntity.getId(), processedEntity); // appRules集合中也保存一份 appRules.computeIfAbsent(processedEntity.getApp(), v -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>(32)) .put(processedEntity.getId(), processedEntity); } return processedEntity; } 在看看publishRules()是如何调用微服务端进行规则更新的
- 从machineRules 对应微服务ip+port机器的集合 中把规则取出来
List<FlowRuleEntity> rules - 发送请求给微服务端
http://ip:8719/setRules
private CompletableFuture<Void> publishRules(String app, String ip, Integer port) { // 通过machineRules 对应微服务ip+port机器的集合 中把规则取出来 // 控制台的规则实体对象是FlowRuleEntity,而微服务端的规则实体对象是FlowRule List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = repository.findAllByMachine(MachineInfo.of(app, ip, port)); // 发送请求给微服务端 return sentinelApiClient.setFlowRuleOfMachineAsync(app, ip, port, rules); } // 方法调用 public CompletableFuture<Void> setFlowRuleOfMachineAsync(String app, String ip, int port, List<FlowRuleEntity> rules) { return setRulesAsync(app, ip, port, FLOW_RULE_TYPE, rules); } private CompletableFuture<Void> setRulesAsync(String app, String ip, int port, String type, List<? extends RuleEntity> entities) { try { AssertUtil.notNull(entities, "rules cannot be null"); AssertUtil.notEmpty(app, "Bad app name"); AssertUtil.notEmpty(ip, "Bad machine IP"); AssertUtil.isTrue(port > 0, "Bad machine port"); // 请求参数data // toRule()方法中会把控制台的规则实体对象转换为微服务端的规则实体对象 // 以流控为例 控制台的规则实体对象是FlowRuleEntity,而微服务端的规则实体对象是FlowRule String data = JSON.toJSONString( entities.stream().map(r -> r.toRule()).collect(Collectors.toList())); Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>(2); params.put("type", type); params.put("data", data); // 想微服务端发送请求 SET_RULES_PATH = "setRules" // 所以调用微服务的url是 http://ip:8719/setRules ,微服务端启动时8719端口如果被占用则会往后自增,继续找端口 // 这里就和上面的服务端接收控制台请求串联起来了 return executeCommand(app, ip, port, SET_RULES_PATH, params, true) .thenCompose(r -> { if ("success".equalsIgnoreCase(r.trim())) { return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null); } return AsyncUtils.newFailedFuture(new CommandFailedException(r)); }); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("setRulesAsync API failed, type={}", type, e); return AsyncUtils.newFailedFuture(e); } } 总结
微服务端
微服务端 规则实体对象:
FlowRule微服务端 缓存流控规则管理器:
FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap()微服务端 保存规则的集合定义
Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = new HashMap<>()微服务端 加载规则进内存
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
控制台端
处理请求 FlowControllerV1 /v1/flow/rule
规则实体: FlowRuleEntity
缓存规则: 基于内存模式 allRules machineRules appRules
接口: RuleRepository 规则持久化的扩展点(考虑)
发布缓存: 推送到微服务端内存中
- 请求参数转换: FlowRuleEntity ——》FlowRule
- 发起请求:
http://ip:8719/setRules
微服务端接收请求:
ModifyRulesCommandHandler#handle
加载规则: FlowRuleManager.loadRules(flowRules)
接口: WritableDataSource 规则持久化的扩展点
pull拉模式
pull 模式的数据源(如本地文件、RDBMS 等)一般是可写入的。使用时需要在客户端注册数据源:
- 将对应的读数据源注册至对应的
RuleManager - 将写数据源注册至 transport 的
WritableDataSourceRegistry中。
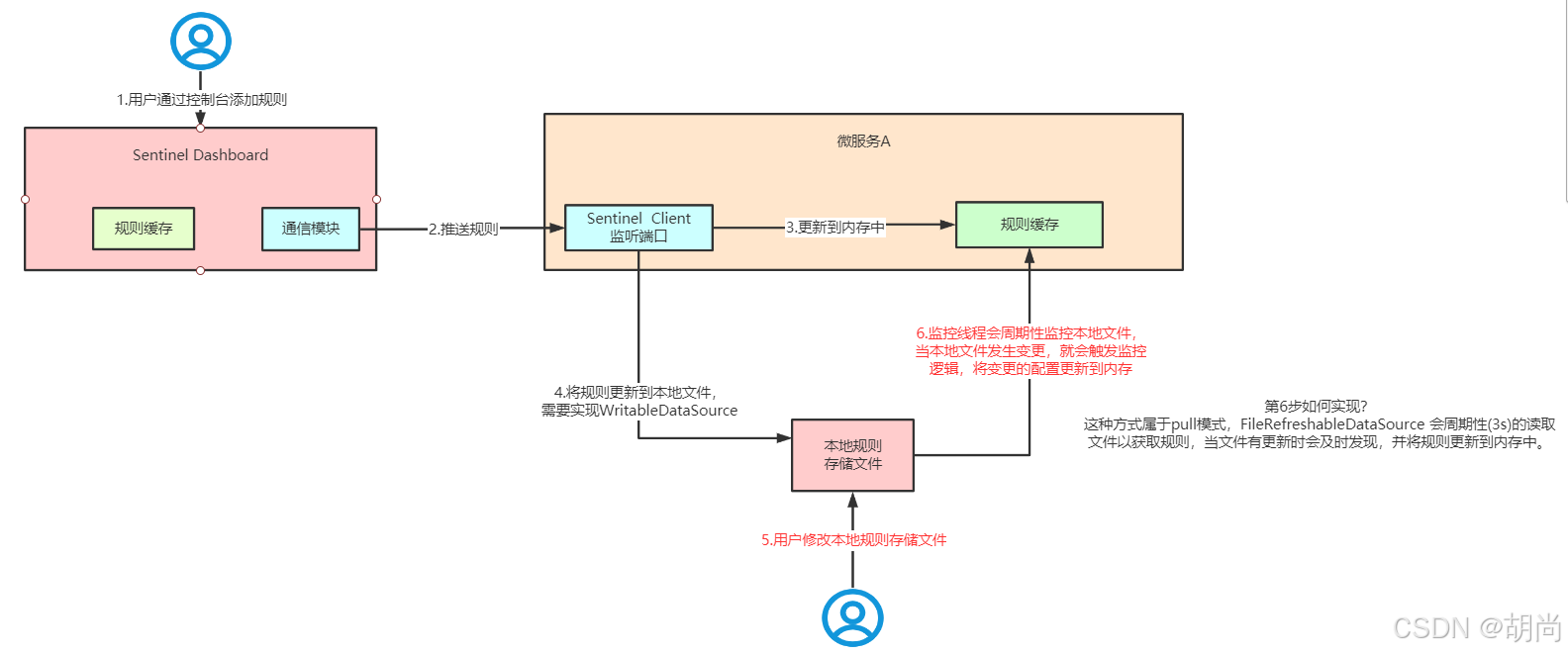
首先 Sentinel 控制台通过 API 将规则推送至客户端并更新到内存中,接着注册的写数据源会将新的规则保存到本地的文件中。
当我们直接修改本地文件,读数据源的线程会定期3s读取文件,将变更的配置更新到内存中
使用 pull 模式的数据源时一般不需 要对 Sentinel 控制台进行改造。这种实现方法好处是简单,坏处是无法保证监控数据的一致性。
官方demo
在sentinel的源码中,它其实提供了一些写文件的demo,位置在下图的位置
具体实现的核心的代码就是下面这个类
import java.io.File; import java.util.List; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.FileRefreshableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.FileWritableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.ReadableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.WritableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference; public class FileDataSourceInit implements InitFunc { @Override public void init() throws Exception { //定义文件路径 String flowRuleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + File.separator + "sentinel" + File.separator + "rules"; String flowRuleFile = "flowRule.json"; String flowRulePath = flowRuleDir + File.separator + flowRuleFile; // 将对应的读数据源注册至对应的FlowRuleManager ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> ds = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( flowRulePath, source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}) ); FlowRuleManager.register2Property(ds.getProperty()); // 将写数据源注册至 transport 的WritableDataSourceRegistry中 WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> wds = new FileWritableDataSource<>(flowRulePath, this::encodeJson); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(wds); } private <T> String encodeJson(T t) { return JSON.toJSONString(t); } } 我们先看看将对应的读数据源注册至对应的FlowRuleManager这一块的逻辑,读数据源FileRefreshableDataSource它的结构如下
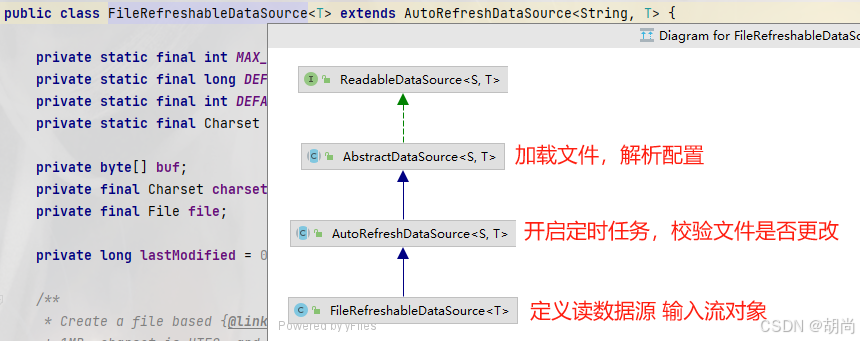
关键代码
// FileRefreshableDataSource类方法 定义文件输入流 校验文件是否更新 public String readSource() throws Exception { // ...... // 创建文件输入流,文件的最后修改时间进行判断,文件修改后父类就会调用到这里来 FileInputStream inputStream = null; try { inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); FileChannel channel = inputStream.getChannel(); if (channel.size() > buf.length) { throw new IllegalStateException(file.getAbsolutePath() + " file size=" + channel.size() + ", is bigger than bufSize=" + buf.length + ". Can't read"); } int len = inputStream.read(buf); return new String(buf, 0, len, charset); } finally { // ...... } } // 根据文件最后的修改时间进行判断 protected boolean isModified() { long curLastModified = file.lastModified(); if (curLastModified != this.lastModified) { this.lastModified = curLastModified; return true; } return false; } //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // AutoRefreshDataSource 中间父类方法 。 开启线程任务 调用父类方法 加载配置 + 更新配置 private void startTimerService() { // 创建只有一个线程的线程池 service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1,new NamedThreadFactory("sentinel-datasource-auto-refresh-task", true)); // 每隔3s执行一次定时任务 service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { // 调用子类方法 获取文件的最后修改时间进行判断 if (!isModified()) { return; } // 调用父类方法 加载配置 T newValue = loadConfig(); // 更新配置 getProperty().updateValue(newValue); } catch (Throwable e) { RecordLog.info("loadConfig exception", e); } } }, recommendRefreshMs, recommendRefreshMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } //--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // AbstractDataSource定级父类方法。 调用子类的readSource()方法,并解析配置 public T loadConfig() throws Exception { return loadConfig(readSource()); } public T loadConfig(S conf) throws Exception { // 解析配置 T value = parser.convert(conf); return value; } 我们在看看将写数据源注册至 transport 的WritableDataSourceRegistry中。点进去就会发现这里会和我们微服务端接收控制台请求时处理请求串联起来
我们这边保存写数据源,而微服务端每次接收到控制台的规则更改请求后,都会获取写数据源进行相应的写入操作。
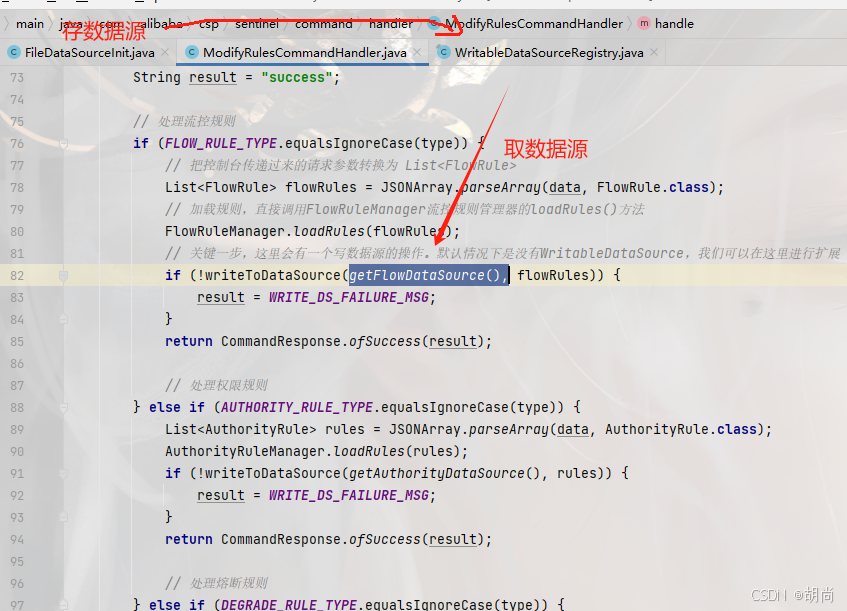
所以最核心的代码就是下面这一块
public void init() throws Exception { //定义文件路径 String flowRuleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + File.separator + "sentinel" + File.separator + "rules"; String flowRuleFile = "flowRule.json"; String flowRulePath = flowRuleDir + File.separator + flowRuleFile; // 将对应的读数据源注册至对应的FlowRuleManager ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> ds = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>( flowRulePath, source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}) ); FlowRuleManager.register2Property(ds.getProperty()); // 将写数据源注册至 transport 的WritableDataSourceRegistry中 WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> wds = new FileWritableDataSource<>(flowRulePath, this::encodeJson); WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(wds); } 这一块的代码如果要和我们SpringCloud微服务进行整合,那应该如何做嘞?
如何整合Spring Cloud
扩展点:
- spi
spring:
beanPostProcessor beanFactoryPostProcessor
SmartInitializingSingleton
ApplicationListener
FactoryBean getObject
springboot
- ApplicationRunner
整合Spring Cloud
我这里使用SPI的方式进行。因为Sentinel本来就有SPI的机制
我们直接在sentinel源码下创建一个子工程,并在META-INF/services目录下创建InitFunc接口对应的文件
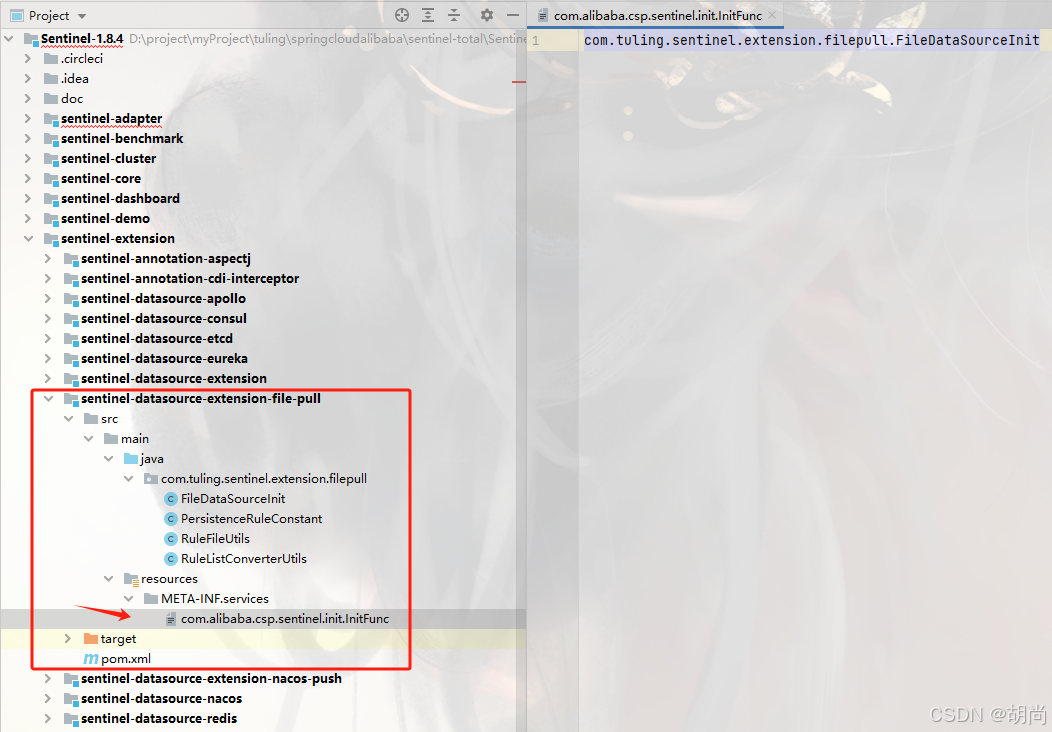
引入的maven依赖如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>sentinel-extension</artifactId> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <version>1.8.4</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>sentinel-datasource-extension-file-pull</artifactId> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-datasource-extension</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-parameter-flow-control</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-source-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.0.1</version> <executions> <execution> <id>attach-sources</id> <goals> <goal>jar</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> 然后编写代码如下,其实就是官方demo的那几行代码的具体实现。
/* * Copyright 1999-2018 Alibaba Group Holding Ltd. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package com.tuling.sentinel.extension.filepull; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.FileRefreshableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.FileWritableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.ReadableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.WritableDataSource; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.util.List; /** * InitFunc实现类,处理dataSource初始化逻辑 * */ public class FileDataSourceInit implements InitFunc { @Override public void init() throws Exception { //创建文件存储目录 RuleFileUtils.mkdirIfNotExits(PersistenceRuleConstant.storePath); //创建规则文件 RuleFileUtils.createFileIfNotExits(PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap); //处理流控规则逻辑 配置读写数据源 dealFlowRules(); // 处理降级规则 dealDegradeRules(); // 处理系统规则 dealSystemRules(); // 处理热点参数规则 dealParamFlowRules(); // 处理授权规则 dealAuthRules(); } private void dealFlowRules() throws FileNotFoundException { String ruleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.FLOW_RULE_PATH).toString(); //创建流控规则的可读数据源 ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource( ruleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.flowRuleListParser ); // 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存 FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>>( ruleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.flowFuleEnCoding ); // 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中. // 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中. WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS); } private void dealDegradeRules() throws FileNotFoundException { //获取规则文件路径 String degradeRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.DEGRAGE_RULE_PATH).toString(); //创建流控规则的可读数据源 ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource( degradeRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.degradeRuleListParse ); // 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存 DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( degradeRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.degradeRuleEnCoding ); // 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中. // 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中. WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS); } private void dealSystemRules() throws FileNotFoundException { //获取规则文件路径 String systemRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.SYSTEM_RULE_PATH).toString(); //创建流控规则的可读数据源 ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource( systemRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.sysRuleListParse ); // 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存 SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( systemRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.sysRuleEnCoding ); // 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中. // 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中. WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS); } private void dealParamFlowRules() throws FileNotFoundException { //获取规则文件路径 String paramFlowRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.HOT_PARAM_RULE).toString(); //创建流控规则的可读数据源 ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource( paramFlowRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.paramFlowRuleListParse ); // 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存 ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty()); WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( paramFlowRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.paramRuleEnCoding ); // 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中. // 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中. ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS); } private void dealAuthRules() throws FileNotFoundException { //获取规则文件路径 String authFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.AUTH_RULE_PATH).toString(); //创建流控规则的可读数据源 ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource( authFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.authorityRuleParse ); // 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存 AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authRuleRDS.getProperty()); //创建流控规则的写数据源 WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>( authFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.authorityEncoding ); // 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中. // 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中. WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authRuleWDS); } } package com.tuling.sentinel.extension.filepull; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; /** * 创建规则持久化目录和文件的工具类 * */ public class RuleFileUtils { public static void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException { File file = new File(filePath); if(!file.exists()) { file.mkdirs(); } } public static void createFileIfNotExits(Map<String,String> ruleFileMap) throws IOException { Set<String> ruleFilePathSet = ruleFileMap.keySet(); Iterator<String> ruleFilePathIter = ruleFilePathSet.iterator(); while (ruleFilePathIter.hasNext()) { String ruleFilePathKey = ruleFilePathIter.next(); String ruleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(ruleFilePathKey).toString(); File ruleFile = new File(ruleFilePath); if(!ruleFile.exists()) { ruleFile.createNewFile(); } } } } package com.tuling.sentinel.extension.filepull; import java.io.File; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * Sentinel 规则持久化 常量配置类 * */ public class PersistenceRuleConstant { /** * 存储文件路径 */ public static final String storePath = System.getProperty("user.home") + File.separator + "sentinel" + File.separator + "rules"; /** * 各种存储sentinel规则映射map */ public static final Map rulesMap = new HashMap<String,String>(); //流控规则文件 public static final String FLOW_RULE_PATH = "flowRulePath"; //降级规则文件 public static final String DEGRAGE_RULE_PATH = "degradeRulePath"; //授权规则文件 public static final String AUTH_RULE_PATH = "authRulePath"; //系统规则文件 public static final String SYSTEM_RULE_PATH = "systemRulePath"; //热点参数文件 public static final String HOT_PARAM_RULE = "hotParamRulePath"; static { rulesMap.put(FLOW_RULE_PATH,storePath+ File.separator +"flowRule.json"); rulesMap.put(DEGRAGE_RULE_PATH,storePath+File.separator +"degradeRule.json"); rulesMap.put(SYSTEM_RULE_PATH,storePath+File.separator +"systemRule.json"); rulesMap.put(AUTH_RULE_PATH,storePath+File.separator +"authRule.json"); rulesMap.put(HOT_PARAM_RULE,storePath+File.separator +"hotParamRule.json"); } } package com.tuling.sentinel.extension.filepull; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.Converter; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule; import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference; import java.util.List; /** * 规则列表解析工具类 * */ public class RuleListConverterUtils { public static final Converter<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleListParser = new Converter<String, List<FlowRule>>() { @Override public List<FlowRule> convert(String source) { return JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}); } }; public static final Converter<String,List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleListParse = new Converter<String, List<DegradeRule>>() { @Override public List<DegradeRule> convert(String source) { return JSON.parseObject(source,new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>(){}); } }; public static final Converter<String,List<SystemRule>> sysRuleListParse = new Converter<String, List<SystemRule>>() { @Override public List<SystemRule> convert(String source) { return JSON.parseObject(source,new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>(){}); } }; public static final Converter<String,List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleListParse = new Converter<String, List<ParamFlowRule>>() { @Override public List<ParamFlowRule> convert(String source) { return JSON.parseObject(source,new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>(){}); } }; public static final Converter<String,List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleParse = new Converter<String, List<AuthorityRule>>() { @Override public List<AuthorityRule> convert(String source) { return JSON.parseObject(source,new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>(){}); } }; public static final Converter<List<FlowRule>,String> flowFuleEnCoding= new Converter<List<FlowRule>,String>() { @Override public String convert(List<FlowRule> source) { return JSON.toJSONString(source); } }; public static final Converter<List<SystemRule>,String> sysRuleEnCoding= new Converter<List<SystemRule>,String>() { @Override public String convert(List<SystemRule> source) { return JSON.toJSONString(source); } }; public static final Converter<List<DegradeRule>,String> degradeRuleEnCoding= new Converter<List<DegradeRule>,String>() { @Override public String convert(List<DegradeRule> source) { return JSON.toJSONString(source); } }; public static final Converter<List<ParamFlowRule>,String> paramRuleEnCoding= new Converter<List<ParamFlowRule>,String>() { @Override public String convert(List<ParamFlowRule> source) { return JSON.toJSONString(source); } }; public static final Converter<List<AuthorityRule>,String> authorityEncoding= new Converter<List<AuthorityRule>,String>() { @Override public String convert(List<AuthorityRule> source) { return JSON.toJSONString(source); } }; } 打一个jar之后上传到公司仓库。
在微服务中引入下面的依赖即可
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId> <artifactId>sentinel-datasource-extension-file-pull</artifactId> <version>1.8.4</version> </dependency> 