阅读量:1
栈
一.栈的概念与结构
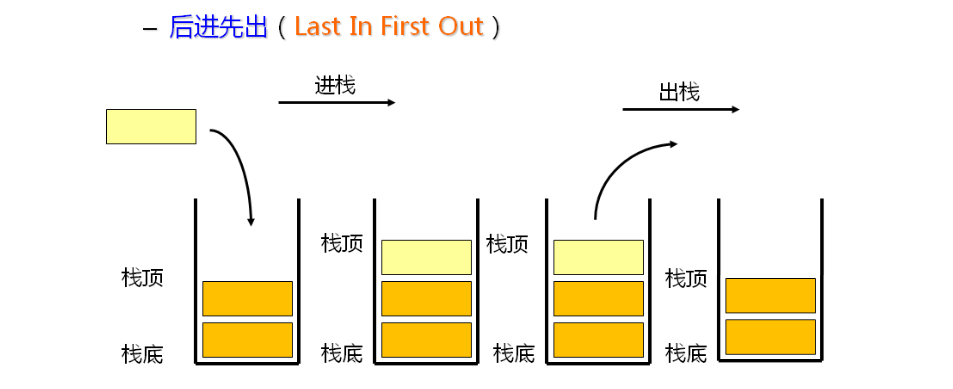
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除
操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)
的原则。
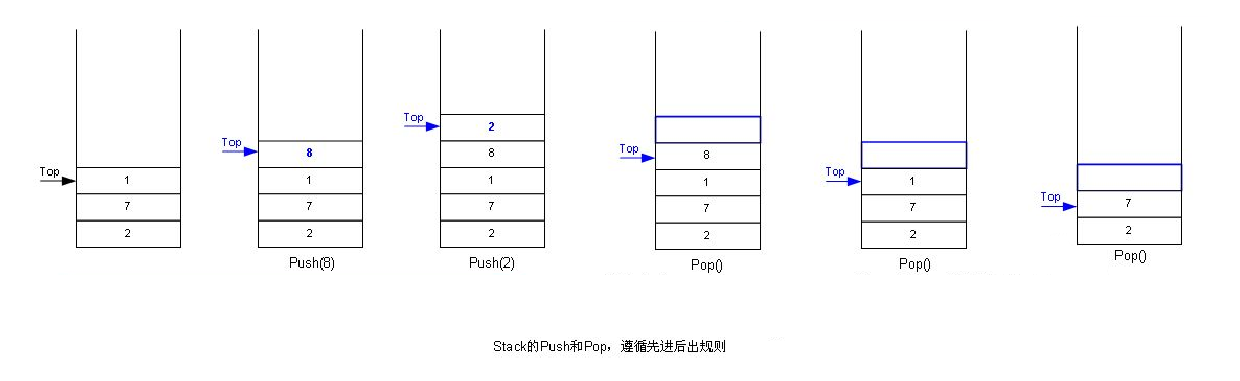
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
二.顺序栈与链栈
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上
插入数据的代价比较小。那是为什么?且听下文分解。
1.顺序栈

2.链栈
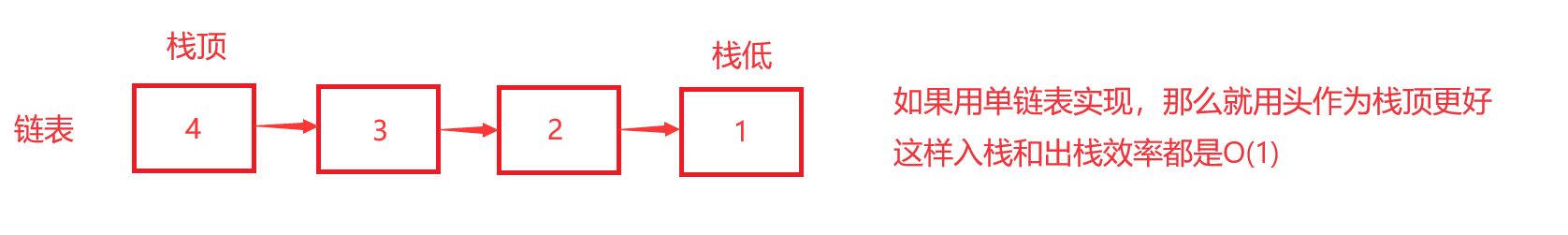
1.单链表栈

将栈顶与栈低换个位置可以解决该问题,如下图:
2.双链表栈
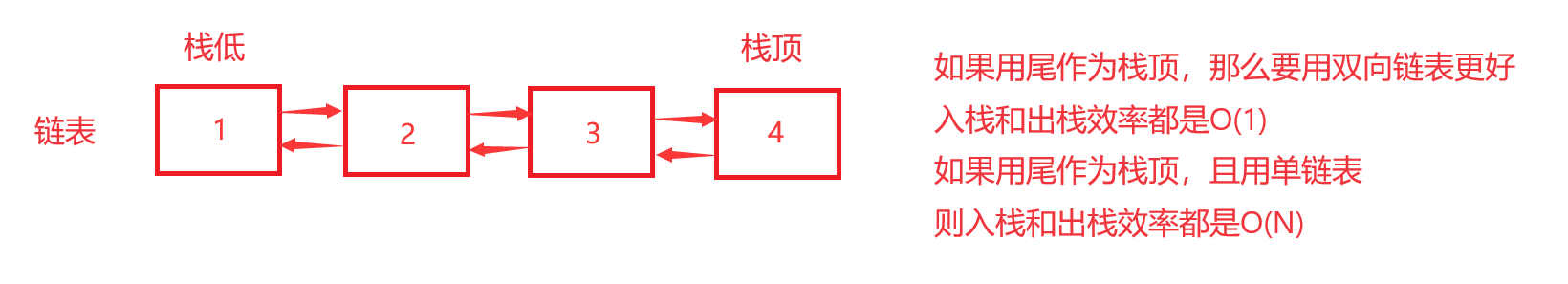
- 由于双向链表比单链表多一个指针,基于节省内存的原由
单链表优于双向链表。 - 数组的效率更优于单链表,原因:链表每一次插入一个数据都要申请一个节点,每次删除一个数据都要释放一个节点,且顺序栈包含数据+容量+栈顶,而链栈包含数据+指针,每个数据都要包含指针,顺序栈较于连栈会省一些内存。
接下来我将实现最优的——>顺序栈
三.顺序栈的实现
会写顺序表,那么实现顺序栈会非常轻松,这里就不一一介绍了,直接上代码。
1.创建顺序栈
typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* arr; //栈空间的首地址 int top; //栈顶 int capacity; //容量 }ST; ST st;//st代表顺序栈 2.栈的初始化
void StackInit(ST* ps) { assert(ps);//断言 ps->arr = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; } 3.检查栈的容量
void CheckCapacity(ST* ps) { assert(ps); //栈满 if (ps->top == ps->capacity) { int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity; STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity); if (tmp == NULL)//空间开辟失败 { perror("realloc fail!"); exit(-1);//退出程序 } //空间开辟成功 ps->arr = tmp; ps->capacity = newCapacity; } } 4.入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) { assert(ps); CheckCapacity(ps); ps->arr[ps->top] = x; ps->top++; } 5.出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0);//栈空,无法出栈,否则下标越界 ps->top--; } 6.获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); return ps->arr[ps->top - 1]; } 7.栈的大小
int StackSize(ST* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top; } 8.栈的判空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top == 0; } 9.栈的清空
void StackClear(ST* ps) { assert(ps); ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; } 10.栈的销毁
void StackDestory(ST* ps) { assert(ps); StackClear(ps); free(ps->arr); ps->arr = NULL; } 四.栈的盲区
由于栈的特殊结构,只能遵循后进先出的原则,不允许随便遍历栈,否则就失去了栈的特点,只能用以下的代码得到数据:
while (!StackEmpty(&st)) { printf("%d ", StackTop(&st)); StackPop(&st); } 五.模块化源代码
1.Stack.h
//#pragma once 防止头文件被重复包含 #ifndef __STACK_H__ #define __STACK_H__ #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdbool.h> typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* arr; //栈空间的首地址 int top; //栈顶 int capacity; //容量 }ST; void StackInit(ST* ps);//栈的初始化 void CheckCapacity(ST* ps);//检查栈的容量 void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//入栈 void StackPop(ST* ps);//出栈 STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);//获取栈顶元素 int StackSize(ST* ps);//获取栈的长度 bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);//栈的判空 void StackClear(ST* ps);//栈的清空 void StackDestory(ST* ps);//栈的销毁 #endif 2.Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"Stack.h" void StackInit(ST* ps) { assert(ps);//断言 ps->arr = NULL; ps->capacity = 0; ps->top = 0; } void CheckCapacity(ST* ps) { assert(ps); //栈满 if (ps->top == ps->capacity) { int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity; STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity); if (tmp == NULL)//空间开辟失败 { perror("realloc fail!"); exit(-1);//退出程序 } //空间开辟成功 ps->arr = tmp; ps->capacity = newCapacity; } } void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) { assert(ps); CheckCapacity(ps); ps->arr[ps->top] = x; ps->top++; } void StackPop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0);//栈空,无法出栈,否则下标越界 ps->top--; } STDataType StackTop(ST* ps) { assert(ps); assert(ps->top > 0); return ps->arr[ps->top - 1]; } int StackSize(ST* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top; } bool StackEmpty(ST* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->top == 0; } void StackClear(ST* ps) { assert(ps); ps->top = 0; ps->capacity = 0; } void StackDestory(ST* ps) { assert(ps); StackClear(ps); free(ps->arr); ps->arr = NULL; } 3.test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"Stack.h" enum { EXIT, PUSH, POP, TOP, SIZE, EMPTY, CLEAR }; void Menu() { printf("***************栈**************\n"); printf("****1.入栈 2.出栈****\n"); printf("****3.栈顶 4.大小****\n"); printf("****5.判空 6.清空****\n"); printf("****0.退出 ******\n"); printf("*******************************\n"); } int main() { ST st; StackInit(&st); int select = 0; STDataType value; bool flag; do { Menu(); printf("请选择您的操作:"); scanf("%d", &select); switch (select) { case EXIT: printf("退出栈!\n"); break; case PUSH: printf("请输入您要入栈的值:"); scanf("%d", &value); StackPush(&st, value); break; case POP: StackPop(&st); break; case TOP: value = StackTop(&st); printf("栈顶元素:%d\n", value); break; case SIZE: printf("栈的大小为:%d\n", StackSize(&st)); break; case EMPTY: flag = StackEmpty(&st); if (flag) { printf("栈为空!\n"); } else { printf("栈不为空!\n"); } break; case CLEAR: StackClear(&st); break; default: printf("输入错误,请重新输入!\n"); break; } } while (select); StackDestory(&st); return 0; } 创作不易,如果能帮到你的话能赏个三连吗?感谢啦!!!
