阅读量:2
MobileNetv2模型原理介绍
前言
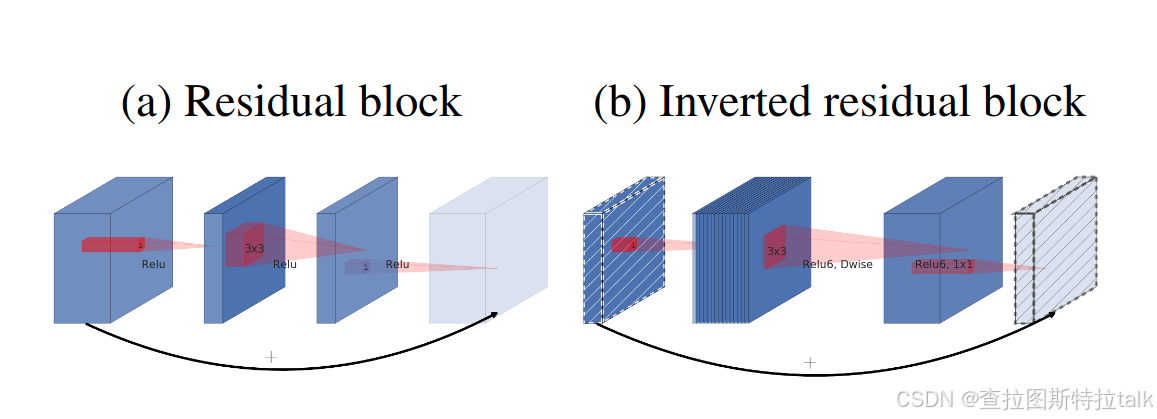
MobileNet是2017年由Google团队提出的轻量级CNN网络,专注于移动端、嵌入式或IoT设备。它使用深度可分离卷积的思想来减小模型参数与运算量,同时引入宽度系数和分辨率系数以满足不同应用场景的需求。MobileNetV2则采用倒残差结构和Linear Bottlenecks来优化模型,提高准确率并缩小模型尺寸。
 操作步骤
操作步骤
数据加载
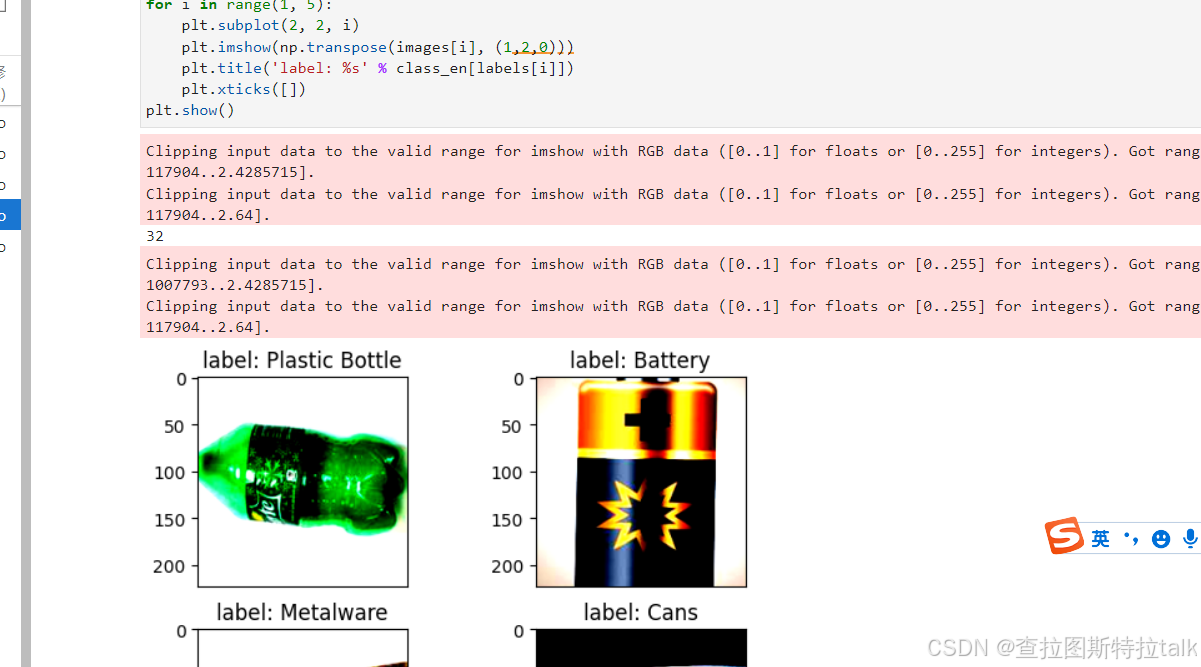
import math import numpy as np import os import random from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from easydict import EasyDict from PIL import Image import numpy as np import mindspore.nn as nn from mindspore import ops as P from mindspore.ops import add from mindspore import Tensor import mindspore.common.dtype as mstype import mindspore.dataset as de import mindspore.dataset.vision as C import mindspore.dataset.transforms as C2 import mindspore as ms from mindspore import set_context, nn, Tensor, load_checkpoint, save_checkpoint, export from mindspore.train import Model from mindspore.train import Callback, LossMonitor, ModelCheckpoint, CheckpointConfig os.environ['GLOG_v'] = '3' # Log level includes 3(ERROR), 2(WARNING), 1(INFO), 0(DEBUG). os.environ['GLOG_logtostderr'] = '0' # 0:输出到文件,1:输出到屏幕 os.environ['GLOG_log_dir'] = '../../log' # 日志目录 os.environ['GLOG_stderrthreshold'] = '2' # 输出到目录也输出到屏幕:3(ERROR), 2(WARNING), 1(INFO), 0(DEBUG). set_context(mode=ms.GRAPH_MODE, device_target="CPU", device_id=0) # 设置采用图模式执行,设备为Ascend## 垃圾分类数据集标签,以及用于标签映射的字典。 garbage_classes = { '干垃圾': ['贝壳', '打火机', '旧镜子', '扫把', '陶瓷碗', '牙刷', '一次性筷子', '脏污衣服'], '可回收物': ['报纸', '玻璃制品', '篮球', '塑料瓶', '硬纸板', '玻璃瓶', '金属制品', '帽子', '易拉罐', '纸张'], '湿垃圾': ['菜叶', '橙皮', '蛋壳', '香蕉皮'], '有害垃圾': ['电池', '药片胶囊', '荧光灯', '油漆桶'] } class_cn = ['贝壳', '打火机', '旧镜子', '扫把', '陶瓷碗', '牙刷', '一次性筷子', '脏污衣服', '报纸', '玻璃制品', '篮球', '塑料瓶', '硬纸板', '玻璃瓶', '金属制品', '帽子', '易拉罐', '纸张', '菜叶', '橙皮', '蛋壳', '香蕉皮', '电池', '药片胶囊', '荧光灯', '油漆桶'] class_en = ['Seashell', 'Lighter','Old Mirror', 'Broom','Ceramic Bowl', 'Toothbrush','Disposable Chopsticks','Dirty Cloth', 'Newspaper', 'Glassware', 'Basketball', 'Plastic Bottle', 'Cardboard','Glass Bottle', 'Metalware', 'Hats', 'Cans', 'Paper', 'Vegetable Leaf','Orange Peel', 'Eggshell','Banana Peel', 'Battery', 'Tablet capsules','Fluorescent lamp', 'Paint bucket'] index_en = {'Seashell': 0, 'Lighter': 1, 'Old Mirror': 2, 'Broom': 3, 'Ceramic Bowl': 4, 'Toothbrush': 5, 'Disposable Chopsticks': 6, 'Dirty Cloth': 7, 'Newspaper': 8, 'Glassware': 9, 'Basketball': 10, 'Plastic Bottle': 11, 'Cardboard': 12, 'Glass Bottle': 13, 'Metalware': 14, 'Hats': 15, 'Cans': 16, 'Paper': 17, 'Vegetable Leaf': 18, 'Orange Peel': 19, 'Eggshell': 20, 'Banana Peel': 21, 'Battery': 22, 'Tablet capsules': 23, 'Fluorescent lamp': 24, 'Paint bucket': 25} # 训练超参 config = EasyDict({ "num_classes": 26, "image_height": 224, "image_width": 224, #"data_split": [0.9, 0.1], "backbone_out_channels":1280, "batch_size": 16, "eval_batch_size": 8, "epochs": 10, "lr_max": 0.05, "momentum": 0.9, "weight_decay": 1e-4, "save_ckpt_epochs": 1, "dataset_path": "./data_en", "class_index": index_en, "pretrained_ckpt": "./mobilenetV2-200_1067.ckpt" # mobilenetV2-200_1067.ckpt })对垃圾分类数据集进行数据预处理,包括读取数据集、归一化、修改图像频道等操作。对训练集进行RandomCropDecodeResize、RandomHorizontalFlip、RandomColorAdjust、shuffle等操作,对测试集进行Decode、Resize、CenterCrop等操作。
MobileNetV2模型的训练与测试
训练策略
一般情况下,模型训练时采用静态学习率,如0.01。随着训练步数的增加,模型逐渐趋于收敛,对权重参数的更新幅度应该逐渐降低,以减小模型训练后期的抖动。所以,模型训练时可以采用动态下降的学习率,常见的学习率下降策略有:
__all__ = ['MobileNetV2', 'MobileNetV2Backbone', 'MobileNetV2Head', 'mobilenet_v2'] def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None): if min_value is None: min_value = divisor new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor) if new_v < 0.9 * v: new_v += divisor return new_v class GlobalAvgPooling(nn.Cell): """ Global avg pooling definition. Args: Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> GlobalAvgPooling() """ def __init__(self): super(GlobalAvgPooling, self).__init__() def construct(self, x): x = P.mean(x, (2, 3)) return x class ConvBNReLU(nn.Cell): """ Convolution/Depthwise fused with Batchnorm and ReLU block definition. Args: in_planes (int): Input channel. out_planes (int): Output channel. kernel_size (int): Input kernel size. stride (int): Stride size for the first convolutional layer. Default: 1. groups (int): channel group. Convolution is 1 while Depthiwse is input channel. Default: 1. Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> ConvBNReLU(16, 256, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=1) """ def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1): super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__() padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 in_channels = in_planes out_channels = out_planes if groups == 1: conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, pad_mode='pad', padding=padding) else: out_channels = in_planes conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, pad_mode='pad', padding=padding, group=in_channels) layers = [conv, nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes), nn.ReLU6()] self.features = nn.SequentialCell(layers) def construct(self, x): output = self.features(x) return output class InvertedResidual(nn.Cell): """ Mobilenetv2 residual block definition. Args: inp (int): Input channel. oup (int): Output channel. stride (int): Stride size for the first convolutional layer. Default: 1. expand_ratio (int): expand ration of input channel Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> ResidualBlock(3, 256, 1, 1) """ def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride, expand_ratio): super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__() assert stride in [1, 2] hidden_dim = int(round(inp * expand_ratio)) self.use_res_connect = stride == 1 and inp == oup layers = [] if expand_ratio != 1: layers.append(ConvBNReLU(inp, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1)) layers.extend([ ConvBNReLU(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, stride=stride, groups=hidden_dim), nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, has_bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(oup), ]) self.conv = nn.SequentialCell(layers) self.cast = P.Cast() def construct(self, x): identity = x x = self.conv(x) if self.use_res_connect: return P.add(identity, x) return x class MobileNetV2Backbone(nn.Cell): """ MobileNetV2 architecture. Args: class_num (int): number of classes. width_mult (int): Channels multiplier for round to 8/16 and others. Default is 1. has_dropout (bool): Is dropout used. Default is false inverted_residual_setting (list): Inverted residual settings. Default is None round_nearest (list): Channel round to . Default is 8 Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> MobileNetV2(num_classes=1000) """ def __init__(self, width_mult=1., inverted_residual_setting=None, round_nearest=8, input_channel=32, last_channel=1280): super(MobileNetV2Backbone, self).__init__() block = InvertedResidual # setting of inverted residual blocks self.cfgs = inverted_residual_setting if inverted_residual_setting is None: self.cfgs = [ # t, c, n, s [1, 16, 1, 1], [6, 24, 2, 2], [6, 32, 3, 2], [6, 64, 4, 2], [6, 96, 3, 1], [6, 160, 3, 2], [6, 320, 1, 1], ] # building first layer input_channel = _make_divisible(input_channel * width_mult, round_nearest) self.out_channels = _make_divisible(last_channel * max(1.0, width_mult), round_nearest) features = [ConvBNReLU(3, input_channel, stride=2)] # building inverted residual blocks for t, c, n, s in self.cfgs: output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, round_nearest) for i in range(n): stride = s if i == 0 else 1 features.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, stride, expand_ratio=t)) input_channel = output_channel features.append(ConvBNReLU(input_channel, self.out_channels, kernel_size=1)) self.features = nn.SequentialCell(features) self._initialize_weights() def construct(self, x): x = self.features(x) return x def _initialize_weights(self): """ Initialize weights. Args: Returns: None. Examples: >>> _initialize_weights() """ self.init_parameters_data() for _, m in self.cells_and_names(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels m.weight.set_data(Tensor(np.random.normal(0, np.sqrt(2. / n), m.weight.data.shape).astype("float32"))) if m.bias is not None: m.bias.set_data( Tensor(np.zeros(m.bias.data.shape, dtype="float32"))) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.gamma.set_data( Tensor(np.ones(m.gamma.data.shape, dtype="float32"))) m.beta.set_data( Tensor(np.zeros(m.beta.data.shape, dtype="float32"))) @property def get_features(self): return self.features class MobileNetV2Head(nn.Cell): """ MobileNetV2 architecture. Args: class_num (int): Number of classes. Default is 1000. has_dropout (bool): Is dropout used. Default is false Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> MobileNetV2(num_classes=1000) """ def __init__(self, input_channel=1280, num_classes=1000, has_dropout=False, activation="None"): super(MobileNetV2Head, self).__init__() # mobilenet head head = ([GlobalAvgPooling(), nn.Dense(input_channel, num_classes, has_bias=True)] if not has_dropout else [GlobalAvgPooling(), nn.Dropout(0.2), nn.Dense(input_channel, num_classes, has_bias=True)]) self.head = nn.SequentialCell(head) self.need_activation = True if activation == "Sigmoid": self.activation = nn.Sigmoid() elif activation == "Softmax": self.activation = nn.Softmax() else: self.need_activation = False self._initialize_weights() def construct(self, x): x = self.head(x) if self.need_activation: x = self.activation(x) return x def _initialize_weights(self): """ Initialize weights. Args: Returns: None. Examples: >>> _initialize_weights() """ self.init_parameters_data() for _, m in self.cells_and_names(): if isinstance(m, nn.Dense): m.weight.set_data(Tensor(np.random.normal( 0, 0.01, m.weight.data.shape).astype("float32"))) if m.bias is not None: m.bias.set_data( Tensor(np.zeros(m.bias.data.shape, dtype="float32"))) @property def get_head(self): return self.head class MobileNetV2(nn.Cell): """ MobileNetV2 architecture. Args: class_num (int): number of classes. width_mult (int): Channels multiplier for round to 8/16 and others. Default is 1. has_dropout (bool): Is dropout used. Default is false inverted_residual_setting (list): Inverted residual settings. Default is None round_nearest (list): Channel round to . Default is 8 Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> MobileNetV2(backbone, head) """ def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, width_mult=1., has_dropout=False, inverted_residual_setting=None, \ round_nearest=8, input_channel=32, last_channel=1280): super(MobileNetV2, self).__init__() self.backbone = MobileNetV2Backbone(width_mult=width_mult, \ inverted_residual_setting=inverted_residual_setting, \ round_nearest=round_nearest, input_channel=input_channel, last_channel=last_channel).get_features self.head = MobileNetV2Head(input_channel=self.backbone.out_channel, num_classes=num_classes, \ has_dropout=has_dropout).get_head def construct(self, x): x = self.backbone(x) x = self.head(x) return x class MobileNetV2Combine(nn.Cell): """ MobileNetV2Combine architecture. Args: backbone (Cell): the features extract layers. head (Cell): the fully connected layers. Returns: Tensor, output tensor. Examples: >>> MobileNetV2(num_classes=1000) """ def __init__(self, backbone, head): super(MobileNetV2Combine, self).__init__(auto_prefix=False) self.backbone = backbone self.head = head def construct(self, x): x = self.backbone(x) x = self.head(x) return x def mobilenet_v2(backbone, head): return MobileNetV2Combine(backbone, head)在进行深度学习模型训练前的准备工作,包括定义训练函数、读取数据、实例化模型、定义优化器和损失函数。其中详细介绍了损失函数和优化器的概念,以及训练过程中损失函数的作用和优化器的使用。同时还说明了在训练MobileNetV2模型时对参数的固定和损失函数的选择,以及训练过程中损失值和精度的变化情况。
