
😄 19年之后由于某些原因断更了三年,23年重新扬帆起航,推出更多优质博文,希望大家多多支持~
🌷 古之立大事者,不惟有超世之才,亦必有坚忍不拔之志
🎐 个人CSND主页——Micro麦可乐的博客
🐥《Docker实操教程》专栏以最新的Centos版本为基础进行Docker实操教程,入门到实战
🌺《RabbitMQ》专栏主要介绍使用JAVA开发RabbitMQ的系列教程,从基础知识到项目实战
🌸《设计模式》专栏以实际的生活场景为案例进行讲解,让大家对设计模式有一个更清晰的理解
💕《Jenkins实战》专栏主要介绍Jenkins+Docker的实战教程,让你快速掌握项目CI/CD,是2024年最新的实战教程
🌞《Spring Boot》专栏主要介绍我们日常工作项目中经常应用到的功能以及技巧,代码样例完整
如果文章能够给大家带来一定的帮助!欢迎关注、评论互动~
Spring Boot整合Redis通过Zset数据类型+定时任务实现延迟队列
前言
本文对应源码下载地址: https://download.csdn.net/download/lhmyy521125/89412365 无需积分
在我们项目开发中,我们经常需要在特定时间后执行某些任务,例如订单超时未支付自动取消、资金余额低于限额提醒、延时消息发送等。延迟队列是一种非常实用的解决方案,而Redis也具备延迟队列的功能,这里博主将和大家分享基于Redis的Zset数据类型+定时任务实现延迟队列
redis常见的实现延迟队列的方案
❶ 通过过期key通知实现
开启redis的key过期通知,然后在业务中给key设置过期时间,到了过期时间后redis会自动的将过期的key消息推送给监听者,从而实现延迟任务
首先redis配置文件开启过期通知
notify-keyspace-events Ex Java项目中通过继承 KeyExpirationEventMessageListener 监听器重写 onMessage 方法实现消息的接收
@Component @Slf4j public class RedisExpireKeyService extends KeyExpirationEventMessageListener { public RedisExpireKeyService(RedisMessageListenerContainer listenerContainer) { super(listenerContainer); } /** * 监听过期的key * */ @Override public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) { String expireKey = message.toString(); //执行具体的业务 System.out.println("监听到key=" + expireKey + ",已经过期"); } } ❷ 通过Zset数据类型+定时任务实现
本文将介绍使用这种方案,这里暂时先不赘述,后面会详细介绍
❸ Redisson实现延迟队列
·Redisson· 提供了 ·RDelayedQueue· 接口来实现延迟队列功能,我们可以通过它轻松实现延迟任务的处理,本质上Redisson提供的延迟队列底层也是基于 Zset 数据结构实现的
博主将在下次再给大家分享基于Redisson实现延迟队列的教程,这里大家只需要先有个概念。
Zset数据延迟队列的原理
延迟队列是一种特殊的队列,其元素在加入队列时会附带一个延迟时间,只有在延迟时间到达之后,元素才会被处理。我们可以利用 Redis 的有序集合(Sorted Set)来实现延迟队列,因为 Redis 的有序集合支持为每个元素设置一个分数(score),并按照分数进行排序。我们将延迟任务的执行时间作为分数,当时间到达时,取出相应的元素进行处理。
实现步骤
- 将任务加入延迟队列:将任务及其执行时间戳作为元素和分数,存入 Redis 的有序集合
- 轮询检查任务:定期检查有序集合中是否有到期的任务
- 处理到期任务:取出到期任务并执行相应操作
开始实现
步骤一:添加依赖
首先,确保你已经安装并配置好了 Redis 服务器,并构建你的 Spring Boot 项目,在pom.xml中引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> 步骤二:配置Redis
在Spring Boot配置文件设置 Redis 的连接参数
spring: #redis redis: # 地址 host: 127.0.0.1 # 端口,默认为6379 port: 6379 # 数据库索引 database: 0 # 密码 password: # 连接超时时间 timeout: 10s lettuce: pool: # 连接池中的最小空闲连接 min-idle: 5 # 连接池中的最大空闲连接 max-idle: 8 # 连接池的最大数据库连接数 max-active: 20 # #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) max-wait: -1ms 步骤三:创建一个简单任务模型
创建一个简单的任务模型 DelayedTask:
import lombok.Data; @Data public class DelayedTask { private String id; private String message; } 步骤四:创建 Redis 配置类
创建一个配置类 RedisConfig 用于配置 RedisTemplate:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; @Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) { RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setConnectionFactory(factory); template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()); return template; } } 步骤五:创建线程池配置类
创建一个配置类 ThreadPoolConfig 用于配置线程池:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; @Configuration @EnableScheduling public class ThreadPoolConfig { @Bean public Executor taskExecutor() { ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); executor.setCorePoolSize(10); executor.setMaxPoolSize(20); executor.setQueueCapacity(500); executor.setThreadNamePrefix("DelayedTaskExecutor-"); executor.initialize(); return executor; } } 步骤六:创建延迟队列服务类
创建 DelayedQueueService 来处理任务的添加和执行,并使用线程池进行调度:
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import javax.annotation.Resource; import java.util.Set; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; @Service public class DelayedQueueService { @Resource private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate; @Resource private Executor taskExecutor; private static final String DELAYED_QUEUE = "delayed_queue"; public void addTask(DelayedTask task, long delay) { long executeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + delay; redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(DELAYED_QUEUE, task, executeTime); System.out.println("添加任务编号: " + task.getId() + " 将在 " + delay + "ms 执行"); } @Scheduled(fixedRate = 1000) public void processTasks() { long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> tasks = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().rangeByScoreWithScores(DELAYED_QUEUE, 0, currentTime); if (tasks != null && !tasks.isEmpty()) { for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> task : tasks) { DelayedTask delayedTask = (DelayedTask) task.getValue(); System.out.println("处理任务: " + delayedTask.getId()); redisTemplate.opsForZSet().remove(DELAYED_QUEUE, delayedTask); taskExecutor.execute(() -> processTask(delayedTask)); } } } private void processTask(DelayedTask task) { // 在这里添加任务处理的逻辑 System.out.println("任务执行: 任务编号" + task.getId() + " + ,message: " + task.getMessage()); } } 步骤七:创建测试Controller
创建一个简单的控制器 TaskController 来测试我们的延迟队列:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class TaskController { @Autowired private DelayedQueueService delayedQueueService; @PostMapping("/addTask") public String addTask(@RequestBody DelayedTask task, @RequestParam long delay) { delayedQueueService.addTask(task, delay); return "任务添加成功"; } } 开始测试
完成上述代码编写后,我们启动 Spring Boot ,使用调试工具进行测试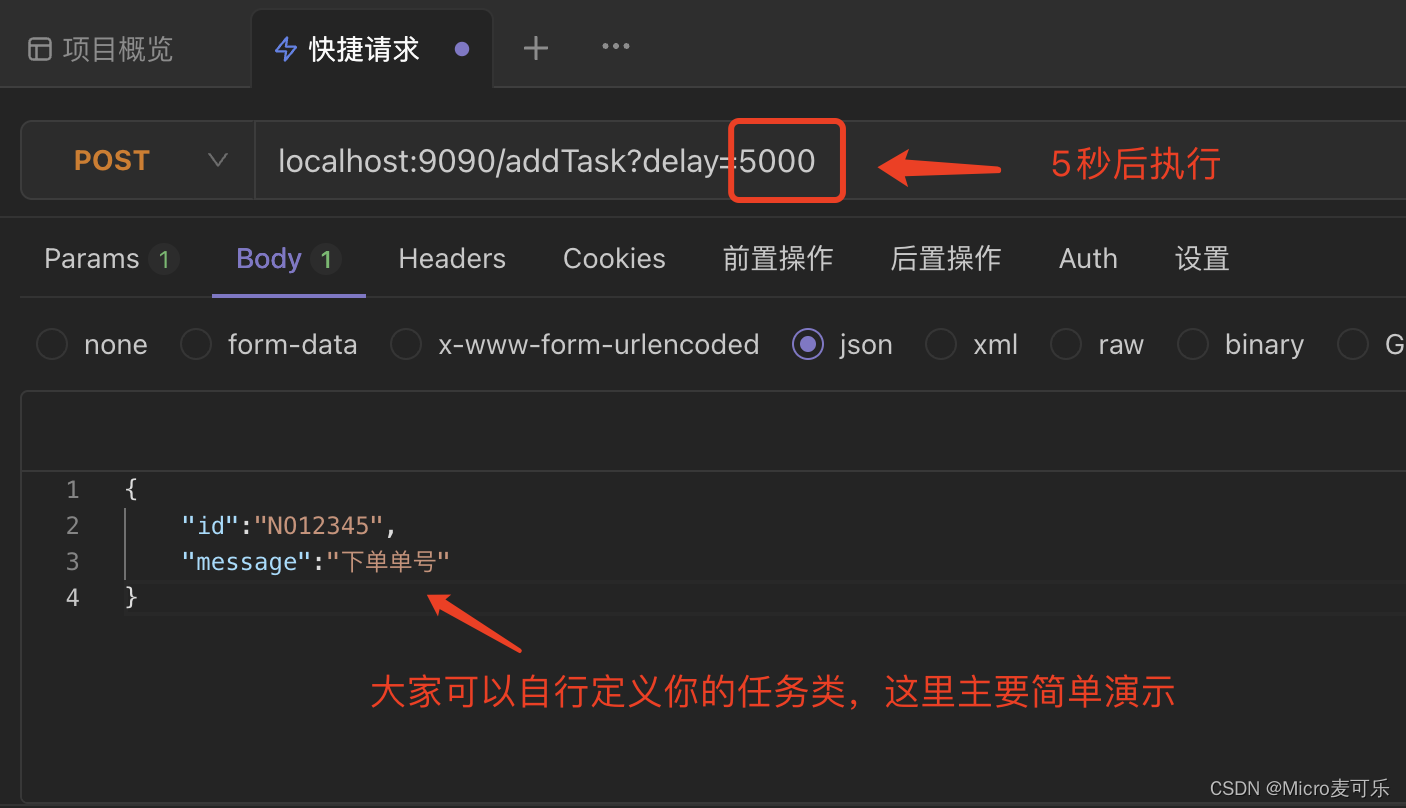
观察控制台输出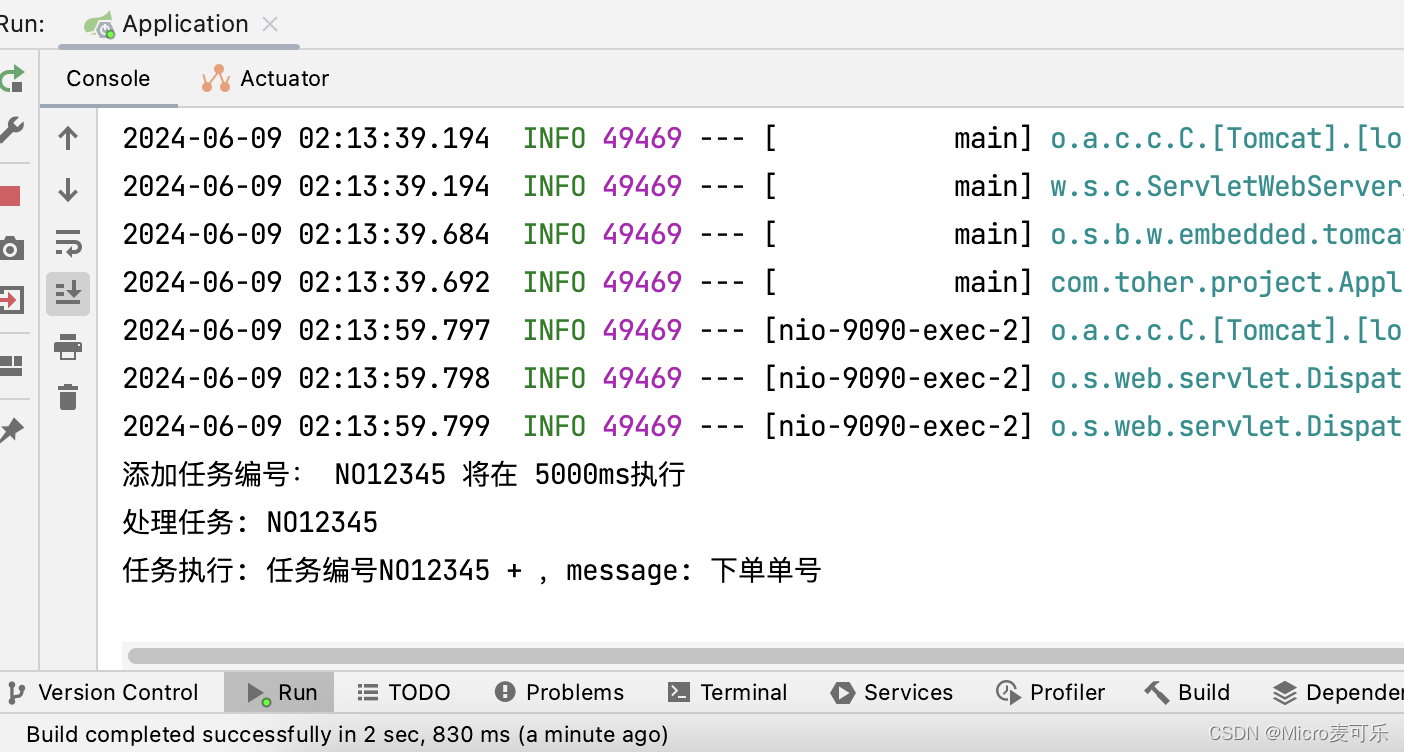
OK,至此我们通过Redis的Zset数据类型+定时任务实现延迟队列的功能已经完成!
总结
到这里相信小伙伴们已经了解了如何使用 Spring Boot 和 Redis 实现一个简单的延迟队列,并使用线程池来执行定时任务以提高效率。延迟队列能够有效地处理需要在特定时间点或延迟一段时间后执行的任务。在实际应用中,可以根据需求进一步扩展和优化该方案,例如增加任务重试机制、错误处理等。
本文的代码主要是演示使用,小伙伴们可以根据自己业务需求进行修改升级。如果本文对您有所帮助,希望 一键三连 给博主一点点鼓励,如果您有任何疑问或建议,请随时留言讨论。

