阅读量:1
目录
c.动态内存空间的开辟(malloc,calloc,realloc).
零.必备知识
a.顺序表的底层是数组.
b.数组在内存中是连续存放的.
c.动态内存空间的开辟(malloc,calloc,realloc).
一.顺序表的定义与实现
注:具体解释都在注释中(在代码中具体分析!)
1.1 顺序表的定义
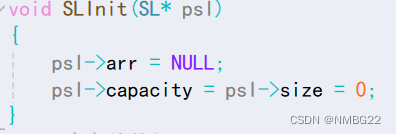
1.2 顺序表的初始化
1.3 顺序表的销毁
1.4 顺序表容量的检查与调整(最关键的部分)
1.5 顺序表的尾插
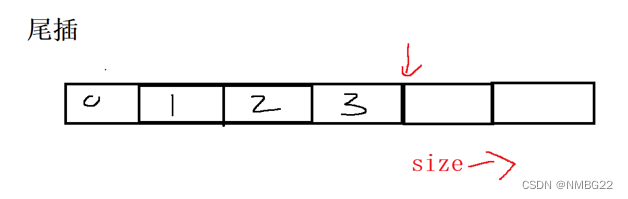
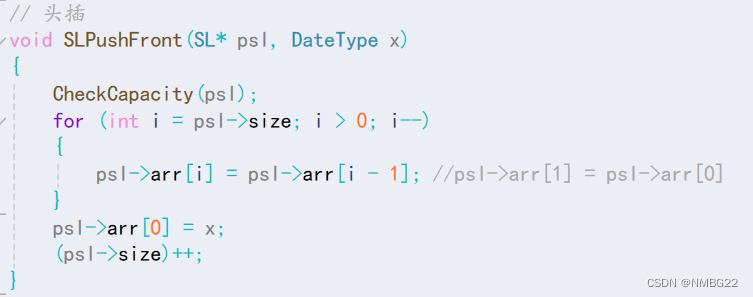
1.6 顺序表的头插
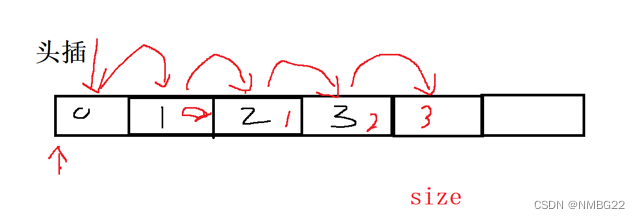
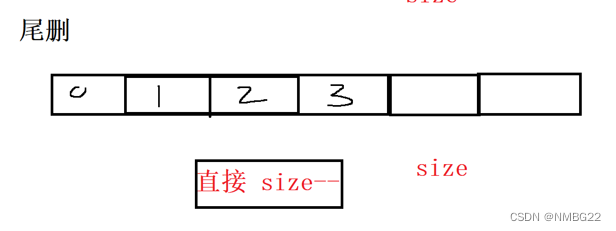
1.7 顺序表的尾删
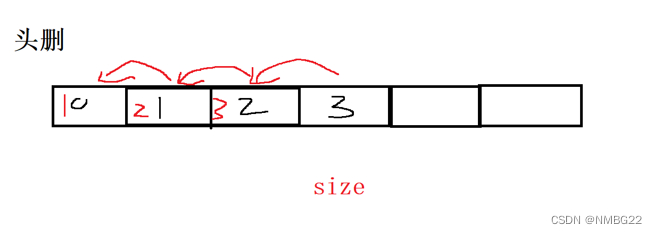
1.8 顺序表的头删
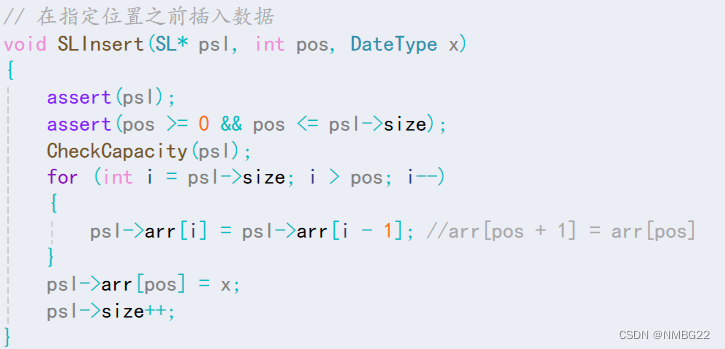
1.9 顺序表中在指定位置之前插入数据
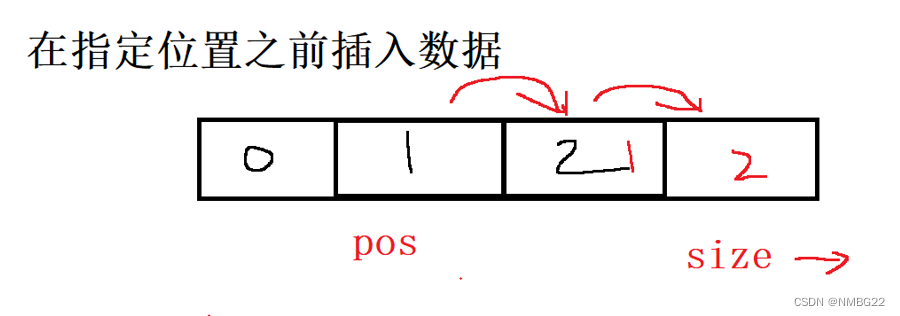
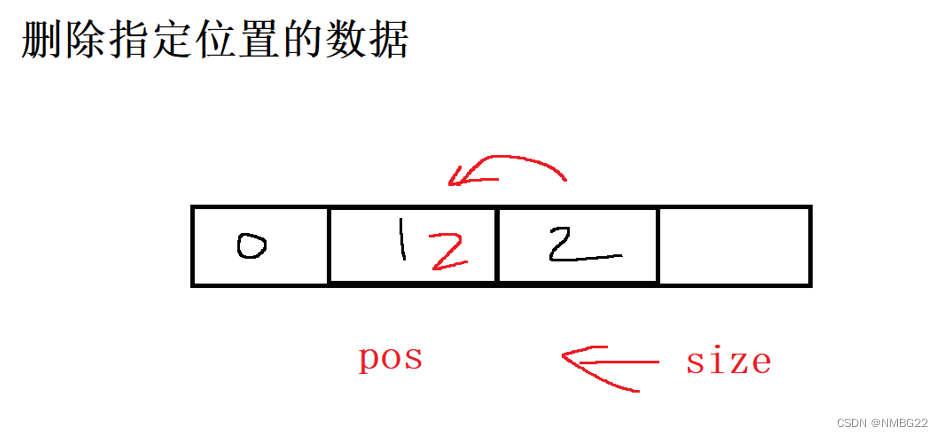
1.10 删除指定位置的数据
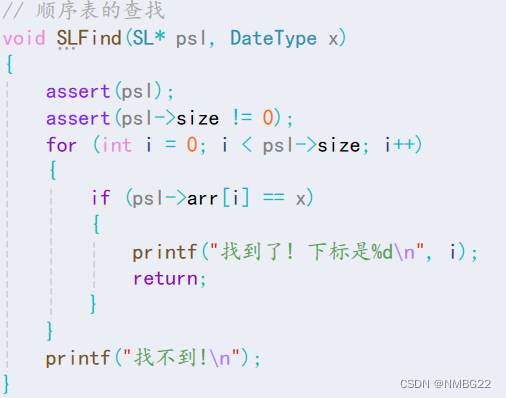
1.11 顺序表中查找指定数据
二.顺序表源码
SeqList.h
#pragma once #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <assert.h> 静态顺序表 //struct SeqList //{ // int arr[100]; // int size; //}; // 动态顺序表的定义 typedef int DateType; //数据类型 typedef struct SeqList { DateType* arr; int size; //数组中的有效元素个数 int capacity; //数组的总容量 }SL; // 顺序表的初始化 void SLInit(SL* psl); // 顺序表的销毁 void SLDestroy(SL* psl); // 打印检查 void SLprint(SL sl); // 容量检查与调整 void CheckCapacity(SL* psl); // 尾插-头插 void SLPushBack(SL* psl, DateType x); void SLPushFront(SL* psl, DateType x); // 尾删-头删 void SLPopBack(SL* psl); void SLPopFront(SL* psl); // 在指定位置之前插入数据 void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, DateType x); //pos:点 // 删除指定位置的数据 void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos); // 顺序表的查找 void SLFind(SL psl, DateType x);SeqList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include "SeqList.h" // 顺序表的初始化 void SLInit(SL* psl) { psl->arr = NULL; psl->size = psl->capacity = 0; } // 顺序表的销毁 void SLDestroy(SL* psl) { if (psl->arr) { free(psl->arr); //释放动态开辟的内存空间 } psl->arr = NULL; psl->size = psl->capacity = 0; } // 容量检查与调整 void CheckCapacity(SL* psl) { if (psl->size == psl->capacity) //空间不够了,需要进行扩容 { int newCapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2; //避免 psl->capacity初始容量为空 DateType* temp = (DateType*)realloc(psl->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(DateType)); if (temp == NULL) //避免因为realloc调整空间失败,而导致psl->arr中的数据被清除 { perror("realloc fail!"); exit(1); } psl->capacity = newCapacity; psl->arr = temp; } } // 尾插 void SLPushBack(SL* psl, DateType x) { CheckCapacity(psl); // 插入 psl->arr[psl->size] = x; psl->size++; } // 头插 void SLPushFront(SL* psl, DateType x) { CheckCapacity(psl); for (int i = psl->size; i > 0; i--) { psl->arr[i] = psl->arr[i - 1]; //psl->arr[1] = psl->arr[0] } psl->arr[0] = x; (psl->size)++; } // 尾删 void SLPopBack(SL* psl) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size); //判断是否为空 (psl->size)--; } // 头删 void SLPopFront(SL* psl) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size); //判断是否为空 for (int i = 0; i < psl->size - 1; i++) { psl->arr[i] = psl->arr[i + 1]; //psl->arr[psl->size - 1] = psl->arr[psl->size - 2] } (psl->size)--; } // 在指定位置之前插入数据 void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, DateType x) { assert(psl); assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size); CheckCapacity(psl); for (int i = psl->size; i > pos; i--) { psl->arr[i] = psl->arr[i - 1]; //arr[pos + 1] = arr[pos] } psl->arr[pos] = x; psl->size++; } // 删除指定位置的数据 void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size != 0); assert(pos >= 0 && pos < psl->size); for (int i = pos; i < psl->size - 1; i++) { psl->arr[i] = psl->arr[i + 1]; //arr[i - 2] = arr[i - 1] } psl->size--; } // 顺序表的查找 void SLFind(SL* psl, DateType x) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size != 0); for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++) { if (psl->arr[i] == x) { printf("找到了! 下标是%d\n", i); return; } } printf("找不到!\n"); } // 打印 void SLprint(SL sl) { for (int i = 0; i < sl.size; i++) { printf("%d ", sl.arr[i]); } printf("\n"); }