阅读量:2
常用的三种索引方式
Faiss 中有常用的三种索引方式:IndexFlatL2、IndexIVFFlat 和 IndexIVFPQ。
1.IndexFlatL2 - 暴力检索L2:
- 使用欧氏距离(L2)进行精确检索。
- 适用于较小规模的数据集,采用暴力检索的方式,即计算查询向量与所有数据库向量之间的距离,然后返回相似度最高的前 k 个向量。
import faiss d = 200 # 向量维度 index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d) # 构建索引 data = ... # 添加数据 index.add(data) # 添加数据到索引 k = 500 # 返回结果个数 query = ... # 查询向量 dis, ind = index.search(query, k) # 查询相似内容 2. IndexIVFFlat - 倒排索引,加速:
- 使用倒排索引结构,将数据集划分为多个聚类空间,以加速搜索。
- 在查询阶段,首先定位到可能包含相似向量的聚类中心,然后在该聚类中心附近进行精确搜索。
import faiss d = 200 # 向量维度 nlist = 10000 # 聚类空间 k = 500 # 返回结果个数 quantizer = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d) # 量化器 index = faiss.IndexIVFFlat(quantizer, d, nlist) # 构建索引 index.nprobe = 20 # 查找聚类中心的个数 index.train(data) # 训练 index.add(data) # 添加数据到索引 dis, ind = index.search(query, k) # 查询相似内容 3. IndexIVFPQ - 省空间超快:
- 使用 Product Quantization(PQ)技术进行有损压缩,以节省内存。
- 在查询阶段,返回近似结果。
import faiss d = 200 # 向量维度 m = 8 # 空间拆分 nlist = 10000 # 聚类空间 k = 500 # 返回结果个数 quantizer = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d) index = faiss.IndexIVFPQ(quantizer, d, nlist, m, 8) # 每个向量用8 bits 编码 index.nprobe = 20 # 查找聚类中心的个数 index.train(data) # 训练 index.add(data) # 添加数据到索引 dis, ind = index.search(query, k) # 查询相似内容 // https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss/blob/HEAD/tutorial/python/3-IVFPQ.py#L6-L32 import numpy as np d = 64 # dimension nb = 100000 # database size nq = 10000 # nb of queries np.random.seed(1234) # make reproducible xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype('float32') xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. xq = np.random.random((nq, d)).astype('float32') xq[:, 0] += np.arange(nq) / 1000. import faiss nlist = 100 m = 8 k = 4 quantizer = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d) # this remains the same index = faiss.IndexIVFPQ(quantizer, d, nlist, m, 8) # 8 specifies that each sub-vector is encoded as 8 bits index.train(xb) index.add(xb) D, I = index.search(xb[:5], k) # sanity check print(I) print(D) index.nprobe = 10 # make comparable with experiment above D, I = index.search(xq, k) # search print(I[-5:]) 这些索引方法在不同场景下有不同的优势,你可以根据数据集大小、内存限制和搜索速度的需求来选择适当的索引类型。
- Product quantization in Faiss and from scratch
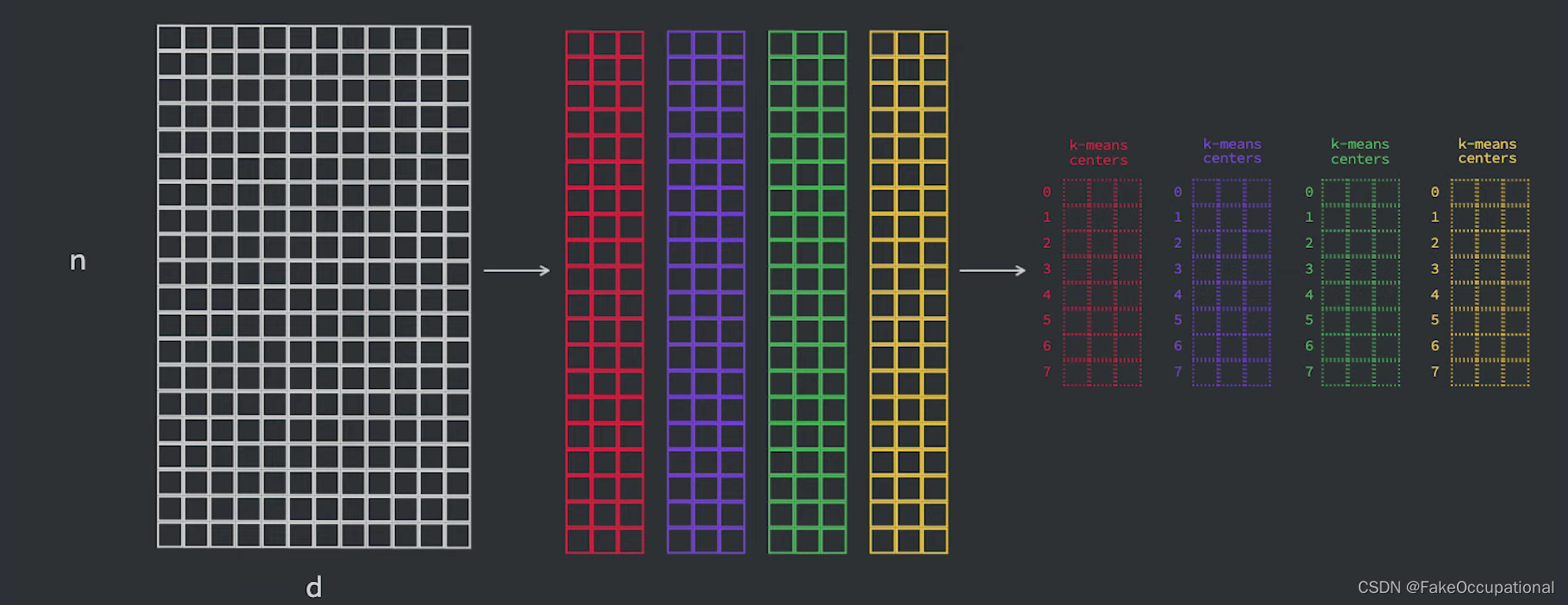
- 乘积量化背后的主要思想是,将采用高维嵌入(其中每个元素都是浮点数)转换为更小的向量,其元素是无符号整数,具体位数通常是八位或一个字节。
- 为了实现这一点,我们首先将向量分成 m 段,然后将每个段映射到某个固定整数。对于 m 个分段中的每个分段都有 m 个单独的估计器,如果我们假设这些估计器已经经过训练,我们可以简单地使用它们将给定分段分配给集群 id,并且该集群 id 是我们将用来表示的数字。
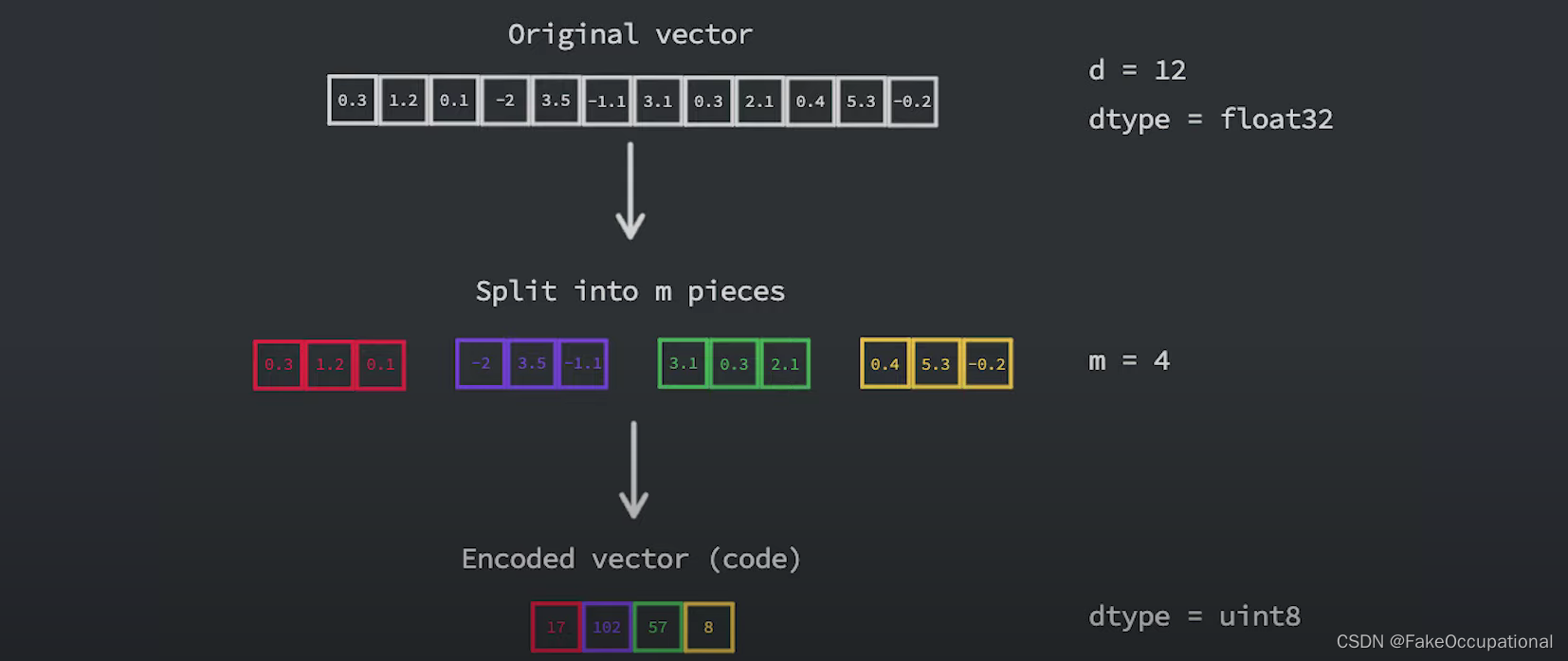
查询过程:

训练的过程:
保存和加载索引
faiss 提供了保存和加载索引的功能,可以将索引保存为文件以便后续重用。这对于避免重新构建索引,以及在不同的程序之间共享索引非常有用。
import faiss import numpy as np # 创建一些随机数据 np.random.seed(42) data = np.random.rand(10, 5).astype('float32') # 创建一个平面索引 index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(5) index.add(data) # 保存索引到文件 faiss.write_index(index, "my_index.index") import faiss import numpy as np # 加载索引 loaded_index = faiss.read_index("my_index.index") # 进行相似性搜索 query_vector = np.random.rand(1, 5).astype('float32') k = 3 D, I = loaded_index.search(query_vector, k) print("相似度最高的{}个向量的索引: {}".format(k, I)) print("对应的相似度分数: {}".format(D)) 清空一个index中的所有数据
import faiss # 假设你已经创建了一个索引 index # 这里以 IndexFlatL2 为例,具体类型根据你的实际情况选择 index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d=128) # 添加一些数据到索引中 data_to_add = [...] # 你的数据 index.add(data_to_add) # 打印添加数据前的索引大小 print("索引大小 (添加数据前):", index.ntotal) # 清空索引中的所有数据 index.reset() # 打印清空数据后的索引大小 print("索引大小 (清空数据后):", index.ntotal) merge
merge_from实现(python)
# 这个例子好像有问题 import faiss # 创建两个示例 IndexIVFPQ 索引 dimension = 64 nlist = 100 nprobe = 32 code_size = 8 # 进行相似性搜索的设置 query_vector = faiss.rand((1, dimension)).astype('float32') k = 3 quantizer = faiss.IndexFlatL2(dimension) index1 = faiss.IndexIVFPQ(quantizer, dimension, nlist, nprobe, 8) # 每个向量用8 bits 编码 index2 = faiss.IndexIVFPQ(quantizer, dimension, nlist, nprobe, 8) # 每个向量用8 bits 编码 # 向索引添加一些示例数据 data1 = faiss.rand((10000, dimension)).astype('float32') data2 = faiss.rand((50000, dimension)).astype('float32') index1.train(data1) index1.add(data1) D, I = index1.search(query_vector, k) print("index1:相似度最高的{}个向量的索引: {}".format(k, I)) print("index1:对应的相似度分数: {}".format(D)) # print("Retrieved Vectors:", data1[I[0]]) index2.train(data2) index2.add(data2) D, I = index2.search(query_vector, k) print("index2:相似度最高的{}个向量的索引: {}".format(k, I)) print("index2:对应的相似度分数: {}".format(D)) # print("Retrieved Vectors:", data2[I[0]]) # 打印每个索引的总数 print("Index 1 total:", index1.ntotal) print("Index 2 total:", index2.ntotal) # 创建一个新的索引,然后将两个索引合并到新的索引中 merged_index = faiss.IndexIVFPQ(quantizer, dimension, nlist, nprobe, 8) merged_index.merge_from(index1,add_id=True) merged_index.merge_from(index2,add_id=True) # 打印合并后的总数 print("Merged Index total:", index1.ntotal) print("Merged Index total:", index1.ntotal) print("Merged Index total:", merged_index.ntotal) D, I = merged_index.search(query_vector, k) print("merged_index合并后:相似度最高的{}个向量的索引: {}".format(k, I)) print("merged_index合并后:对应的相似度分数: {}".format(D)) # index1:相似度最高的3个向量的索引: [[ 0 4722 8480]] # index1:对应的相似度分数: [[0.02087733 6.411026 7.01804 ]] # index2:相似度最高的3个向量的索引: [[ 0 512 33625]] # index2:对应的相似度分数: [[0.02118337 5.254285 5.6290326 ]] # Index 1 total: 10000 # Index 2 total: 50000 # Merged Index total: 0 # Merged Index total: 0 # Merged Index total: 60000 # merged_index合并后:相似度最高的3个向量的索引: [[63 70 1]] # merged_index合并后:对应的相似度分数: [[4.093991 4.093991 4.093991]] - merge_from遍历 PDF 列表。首次创建 Faiss 索引,然后合并其余索引。
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/76421045/how-to-combine-multiple-faiss-indexes-into-one-to-get-a-single-retriever pdfs = [help_doc_name, newsletters_doc_name, supportCases_doc_name] for index, pdf in enumerate(pdfs): content = load_pdf(pdf) if index == 0: faiss_index = FAISS.from_documents(content, OpenAIEmbeddings()) else: faiss_index_i = FAISS.from_documents(content, OpenAIEmbeddings()) faiss_index.merge_from(faiss_index_i) faiss_index.save_local(index_path) retriever = faiss_index.as_retriever( search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 3} ) qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type( llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=retriever, verbose=False ) 另一种实现方式(python)
// https://gist.github.com/mdouze/586746666ef493dbc363aef9266bb990 import numpy as np import faiss def merge_idmap_flat(a, b): a_flat = faiss.downcast_index(a.index) b_flat = faiss.downcast_index(b.index) ab_flat = faiss.IndexFlatL2(a.d) faiss.copy_array_to_vector( np.hstack(( faiss.vector_to_array(a_flat.xb), faiss.vector_to_array(b_flat.xb) )), ab_flat.xb ) ab = faiss.IndexIDMap(ab_flat) ab.referenced = ab_flat # avoid deallocation, not needed in 1.4.0 faiss.copy_array_to_vector( np.hstack(( faiss.vector_to_array(a.id_map), faiss.vector_to_array(b.id_map) )), ab.id_map ) ab_flat.ntotal = ab.ntotal = a.ntotal + b.ntotal return ab code实现(官方库的代码实现逻辑)
使用python定位到最深的实现为IndexIVF类的merge_from方法。这个函数很可能是 faiss 库中的底层实现,通过 swig 工具将 C/C++ 代码包装成 Python 接口。
再TEST宏处进入测试
#include <gtest/gtest.h> // https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss/blob/HEAD/tests/test_merge.cpp#L14 // now use ondisk specific merge https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss/blob/HEAD/tests/test_merge.cpp#L234-L247 TEST(MERGE, merge_flat_ondisk_2) { faiss::IndexShards index_shards(d, false, false); index_shards.own_indices = true; for (int i = 0; i < nindex; i++) { index_shards.add_shard( new faiss::IndexIVFFlat(&cd.quantizer, d, nlist)); } EXPECT_TRUE(index_shards.is_trained); index_shards.add_with_ids(nb, cd.database.data(), cd.ids.data()); int ndiff = compare_merged(&index_shards, false, false); EXPECT_GE(0, ndiff); } - 调用compare_merged
// https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss/blob/HEAD/tests/test_merge.cpp#L88-L144 /// perform a search on shards, then merge and search again and /// compare results. // 定义一个函数,用于在索引分片上进行搜索,合并索引,再次搜索,并比较结果。 int compare_merged( faiss::IndexShards* index_shards, bool shift_ids, bool standard_merge = true) { // 定义用于存储搜索结果的数组 std::vector<idx_t> refI(k * nq); std::vector<float> refD(k * nq); // 在索引分片上执行搜索操作,将结果存储在 refD 和 refI 数组中 index_shards->search(nq, cd.queries.data(), k, refD.data(), refI.data()); Tempfilename filename;// 创建一个临时文件名对象 // 定义新的搜索结果数组 std::vector<idx_t> newI(k * nq); std::vector<float> newD(k * nq); // 根据 standard_merge 的值,选择标准合并方式还是非标准合并方式 if (standard_merge) { // 标准合并方式 for (int i = 1; i < nindex; i++) { faiss::ivflib::merge_into(// 将所有索引分片合并到第一个分片中 index_shards->at(0), index_shards->at(i), shift_ids); } // 同步索引以确保合并的变化得以反映 index_shards->syncWithSubIndexes(); } else { // 非标准合并方式 std::vector<const faiss::InvertedLists*> lists; faiss::IndexIVF* index0 = nullptr; size_t ntotal = 0; // 收集所有分片的倒排列表 for (int i = 0; i < nindex; i++) { auto index_ivf = dynamic_cast<faiss::IndexIVF*>(index_shards->at(i)); assert(index_ivf); if (i == 0) { index0 = index_ivf; } lists.push_back(index_ivf->invlists); ntotal += index_ivf->ntotal; } // 创建一个新的 OnDiskInvertedLists,并将所有倒排列表合并到其中 auto il = new faiss::OnDiskInvertedLists( index0->nlist, index0->code_size, filename.c_str()); il->merge_from(lists.data(), lists.size()); // 替换第一个分片的倒排列表 index0->replace_invlists(il, true); index0->ntotal = ntotal; } // 仅在第一个索引分片上执行搜索操作 index_shards->at(0)->search( nq, cd.queries.data(), k, newD.data(), newI.data()); // 比较搜索结果,计算不同的数量 size_t ndiff = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < k * nq; i++) { if (refI[i] != newI[i]) { ndiff++; } } // 返回不同的数量 return ndiff; } void merge_into(faiss::Index* index0, faiss::Index* index1, bool shift_ids) { // 检查两个索引是否兼容,如果不兼容将引发异常 check_compatible_for_merge(index0, index1); // 将传入的索引强制转换为 IndexIVF 类型 IndexIVF* ivf0 = extract_index_ivf(index0); IndexIVF* ivf1 = extract_index_ivf(index1); // 调用 IndexIVF 类的 merge_from 方法,将 index1 合并到 index0 ivf0->merge_from(*ivf1, shift_ids ? ivf0->ntotal : 0); // 对于 IndexPreTransform 等情况,更新索引总数 index0->ntotal = ivf0->ntotal; index1->ntotal = ivf1->ntotal; } - IndexIVF 的类型定义如下,它继承自两个类:Index 和 IndexIVFInterface。第396行为函数声明:
virtual void merge_from(Index& otherIndex, idx_t add_id) override;,它的实际实现是通过
/** Index based on a inverted file (IVF) * * In the inverted file, the quantizer (an Index instance) provides a * quantization index for each vector to be added. The quantization * index maps to a list (aka inverted list or posting list), where the * id of the vector is stored. * * The inverted list object is required only after trainng. If none is * set externally, an ArrayInvertedLists is used automatically. * * At search time, the vector to be searched is also quantized, and * only the list corresponding to the quantization index is * searched. This speeds up the search by making it * non-exhaustive. This can be relaxed using multi-probe search: a few * (nprobe) quantization indices are selected and several inverted * lists are visited. * * Sub-classes implement a post-filtering of the index that refines * the distance estimation from the query to databse vectors. */ struct IndexIVF : Index, IndexIVFInterface { /// Access to the actual data InvertedLists* invlists = nullptr; // #include <faiss/invlists/InvertedLists.h> bool own_invlists = false; size_t code_size = 0; ///< code size per vector in bytes /** Parallel mode determines how queries are parallelized with OpenMP * * 0 (default): split over queries * 1: parallelize over inverted lists * 2: parallelize over both * 3: split over queries with a finer granularity * * PARALLEL_MODE_NO_HEAP_INIT: binary or with the previous to * prevent the heap to be initialized and finalized */ int parallel_mode = 0; const int PARALLEL_MODE_NO_HEAP_INIT = 1024; /** optional map that maps back ids to invlist entries. This * enables reconstruct() */ DirectMap direct_map; /// do the codes in the invlists encode the vectors relative to the /// centroids? bool by_residual = true; /** The Inverted file takes a quantizer (an Index) on input, * which implements the function mapping a vector to a list * identifier. */ IndexIVF( Index* quantizer, size_t d, size_t nlist, size_t code_size, MetricType metric = METRIC_L2); void reset() override; /// Trains the quantizer and calls train_encoder to train sub-quantizers void train(idx_t n, const float* x) override; /// Calls add_with_ids with NULL ids void add(idx_t n, const float* x) override; /// default implementation that calls encode_vectors void add_with_ids(idx_t n, const float* x, const idx_t* xids) override; /** Implementation of vector addition where the vector assignments are * predefined. The default implementation hands over the code extraction to * encode_vectors. * * @param precomputed_idx quantization indices for the input vectors * (size n) */ virtual void add_core( idx_t n, const float* x, const idx_t* xids, const idx_t* precomputed_idx); /** Encodes a set of vectors as they would appear in the inverted lists * * @param list_nos inverted list ids as returned by the * quantizer (size n). -1s are ignored. * @param codes output codes, size n * code_size * @param include_listno * include the list ids in the code (in this case add * ceil(log8(nlist)) to the code size) */ virtual void encode_vectors( idx_t n, const float* x, const idx_t* list_nos, uint8_t* codes, bool include_listno = false) const = 0; /** Add vectors that are computed with the standalone codec * * @param codes codes to add size n * sa_code_size() * @param xids corresponding ids, size n */ void add_sa_codes(idx_t n, const uint8_t* codes, const idx_t* xids); /** Train the encoder for the vectors. * * If by_residual then it is called with residuals and corresponding assign * array, otherwise x is the raw training vectors and assign=nullptr */ virtual void train_encoder(idx_t n, const float* x, const idx_t* assign); /// can be redefined by subclasses to indicate how many training vectors /// they need virtual idx_t train_encoder_num_vectors() const; void search_preassigned( idx_t n, const float* x, idx_t k, const idx_t* assign, const float* centroid_dis, float* distances, idx_t* labels, bool store_pairs, const IVFSearchParameters* params = nullptr, IndexIVFStats* stats = nullptr) const override; void range_search_preassigned( idx_t nx, const float* x, float radius, const idx_t* keys, const float* coarse_dis, RangeSearchResult* result, bool store_pairs = false, const IVFSearchParameters* params = nullptr, IndexIVFStats* stats = nullptr) const override; /** assign the vectors, then call search_preassign */ void search( idx_t n, const float* x, idx_t k, float* distances, idx_t* labels, const SearchParameters* params = nullptr) const override; void range_search( idx_t n, const float* x, float radius, RangeSearchResult* result, const SearchParameters* params = nullptr) const override; /** Get a scanner for this index (store_pairs means ignore labels) * * The default search implementation uses this to compute the distances */ virtual InvertedListScanner* get_InvertedListScanner( bool store_pairs = false, const IDSelector* sel = nullptr) const; /** reconstruct a vector. Works only if maintain_direct_map is set to 1 or 2 */ void reconstruct(idx_t key, float* recons) const override; /** Update a subset of vectors. * * The index must have a direct_map * * @param nv nb of vectors to update * @param idx vector indices to update, size nv * @param v vectors of new values, size nv*d */ virtual void update_vectors(int nv, const idx_t* idx, const float* v); /** Reconstruct a subset of the indexed vectors. * * Overrides default implementation to bypass reconstruct() which requires * direct_map to be maintained. * * @param i0 first vector to reconstruct * @param ni nb of vectors to reconstruct * @param recons output array of reconstructed vectors, size ni * d */ void reconstruct_n(idx_t i0, idx_t ni, float* recons) const override; /** Similar to search, but also reconstructs the stored vectors (or an * approximation in the case of lossy coding) for the search results. * * Overrides default implementation to avoid having to maintain direct_map * and instead fetch the code offsets through the `store_pairs` flag in * search_preassigned(). * * @param recons reconstructed vectors size (n, k, d) */ void search_and_reconstruct( idx_t n, const float* x, idx_t k, float* distances, idx_t* labels, float* recons, const SearchParameters* params = nullptr) const override; /** Similar to search, but also returns the codes corresponding to the * stored vectors for the search results. * * @param codes codes (n, k, code_size) * @param include_listno * include the list ids in the code (in this case add * ceil(log8(nlist)) to the code size) */ void search_and_return_codes( idx_t n, const float* x, idx_t k, float* distances, idx_t* labels, uint8_t* recons, bool include_listno = false, const SearchParameters* params = nullptr) const; /** Reconstruct a vector given the location in terms of (inv list index + * inv list offset) instead of the id. * * Useful for reconstructing when the direct_map is not maintained and * the inv list offset is computed by search_preassigned() with * `store_pairs` set. */ virtual void reconstruct_from_offset( int64_t list_no, int64_t offset, float* recons) const; /// Dataset manipulation functions size_t remove_ids(const IDSelector& sel) override; void check_compatible_for_merge(const Index& otherIndex) const override; virtual void merge_from(Index& otherIndex, idx_t add_id) override; // returns a new instance of a CodePacker virtual CodePacker* get_CodePacker() const; /** copy a subset of the entries index to the other index * see Invlists::copy_subset_to for the meaning of subset_type */ virtual void copy_subset_to( IndexIVF& other, InvertedLists::subset_type_t subset_type, idx_t a1, idx_t a2) const; ~IndexIVF() override; size_t get_list_size(size_t list_no) const { return invlists->list_size(list_no); } /// are the ids sorted? bool check_ids_sorted() const; /** initialize a direct map * * @param new_maintain_direct_map if true, create a direct map, * else clear it */ void make_direct_map(bool new_maintain_direct_map = true); void set_direct_map_type(DirectMap::Type type); /// replace the inverted lists, old one is deallocated if own_invlists void replace_invlists(InvertedLists* il, bool own = false); /* The standalone codec interface (except sa_decode that is specific) */ size_t sa_code_size() const override; void sa_encode(idx_t n, const float* x, uint8_t* bytes) const override; IndexIVF(); }; merge_from的最终实现
// https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss/blob/HEAD/faiss/invlists/OnDiskInvertedLists.cpp#L569-L636 // 从一组倒排列表中合并数据到当前 OnDiskInvertedLists 对象 size_t OnDiskInvertedLists::merge_from( const InvertedLists** ils, int n_il, bool verbose) { // 确保当前 InvertedLists 对象为空 FAISS_THROW_IF_NOT_MSG( totsize == 0, "works only on an empty InvertedLists"); // 记录每个倒排列表的大小 std::vector<size_t> sizes(nlist); // 遍历所有输入的倒排列表 for (int i = 0; i < n_il; i++) { const InvertedLists* il = ils[i]; // 确保倒排列表的维度和码的大小与当前对象一致 FAISS_THROW_IF_NOT(il->nlist == nlist && il->code_size == code_size); // 统计每个列表的大小 for (size_t j = 0; j < nlist; j++) { sizes[j] += il->list_size(j); } } size_t cums = 0; size_t ntotal = 0; // 根据统计的列表大小更新当前对象的结构 for (size_t j = 0; j < nlist; j++) { ntotal += sizes[j]; lists[j].size = 0; lists[j].capacity = sizes[j]; lists[j].offset = cums; cums += lists[j].capacity * (sizeof(idx_t) + code_size); } // 更新当前对象的总大小 update_totsize(cums); size_t nmerged = 0; double t0 = getmillisecs(), last_t = t0; // 并行处理每个列表 #pragma omp parallel for // OpenMP在循环中实现并行化的预编译关键字(Preprocessor Directives),表示在其后的 for 循环应该在多个线程中并行执行 for (size_t j = 0; j < nlist; j++) { List& l = lists[j]; // 遍历所有输入的倒排列表 for (int i = 0; i < n_il; i++) { const InvertedLists* il = ils[i]; // 获取当前列表在输入倒排列表中的条目数 size_t n_entry = il->list_size(j); // 更新当前列表的大小和内容 l.size += n_entry; update_entries( j, l.size - n_entry, n_entry, ScopedIds(il, j).get(),//根据https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss/blob/HEAD/faiss/invlists/InvertedLists.h#L165-L205的定义看,应该是指向倒排表的指针 ScopedCodes(il, j).get()); } // 确保当前列表的大小与容量相等 assert(l.size == l.capacity); // 在 verbose 模式下,输出合并的进度信息 if (verbose) { #pragma omp critical { nmerged++; double t1 = getmillisecs(); if (t1 - last_t > 500) { printf("merged %zd lists in %.3f s\r", nmerged, (t1 - t0) / 1000.0); fflush(stdout); last_t = t1; } } } } // 输出合并完成的信息 if (verbose) { printf("\n"); } // 返回合并后的总条目数 return ntotal; } 最终的更新实现
void OnDiskInvertedLists::update_entries( size_t list_no, // 表示要更新的倒排列表的编号。 size_t offset, // 表示要更新的列表中的起始位置。 size_t n_entry,// 表示要更新的条目数。 const idx_t* ids_in, // 表示输入的新 ids 数组的指针。 const uint8_t* codes_in) {// 表示输入的新 codes 数组的指针。 // 检查是否为只读状态,如果是,抛出异常 FAISS_THROW_IF_NOT(!read_only); // 如果要更新的条目数为 0,则直接返回 if (n_entry == 0) return; // 获取当前列表的引用 const List& l = lists[list_no]; // 确保更新的范围在合理的范围内 assert(n_entry + offset <= l.size); // 获取当前列表的 ids 数组的指针 idx_t* ids = const_cast<idx_t*>(get_ids(list_no)); // 将输入的 ids_in 复制到列表的相应位置 memcpy(ids + offset, ids_in, sizeof(ids_in[0]) * n_entry); // 获取当前列表的 codes 数组的指针 uint8_t* codes = const_cast<uint8_t*>(get_codes(list_no)); // 将输入的 codes_in 复制到列表的相应位置 memcpy(codes + offset * code_size, codes_in, code_size * n_entry); } 更多功能
https://github1s.com/facebookresearch/faiss-main/tests$ ls CMakeLists.txt test_binary_io.py test_cppcontrib_sa_decode.cpp test_factory.py test_index_binary.py test_local_search_quantizer.py test_omp_threads_py.py test_pq_encoding.cpp test_search_params.py common_faiss_tests.py test_build_blocks.py test_cppcontrib_uintreader.cpp test_fast_scan_ivf.py test_index_composite.py test_lowlevel_ivf.cpp test_ondisk_ivf.cpp test_product_quantizer.py test_simdlib.cpp test_approx_topk.cpp test_clone.py test_dealloc_invlists.cpp test_fast_scan.py test_index.py test_mem_leak.cpp test_oom_exception.py test_RCQ_cropping.cpp test_sliding_ivf.cpp test_autotune.py test_clustering.py test_distances_simd.cpp test_heap.cpp test_io.py test_merge.cpp test_pairs_decoding.cpp test_referenced_objects.py test_standalone_codec.py test_binary_factory.py test_code_distance.cpp test_documentation.py test_hnsw.cpp test_ivflib.py test_merge_index.py test_params_override.cpp test_refine.py test_threaded_index.cpp test_binary_flat.cpp test_contrib.py test_doxygen_documentation.py test_index_accuracy.py test_ivfpq_codec.cpp test_meta_index.py test_partitioning.cpp test_residual_quantizer.py test_transfer_invlists.cpp test_binary_hashindex.py test_contrib_with_scipy.py test_extra_distances.py test_index_binary_from_float.py test_ivfpq_indexing.cpp test_omp_threads.cpp test_partition.py test_rowwise_minmax.py torch_test_contrib.py 缺点
- 不支持动态更新:FAISS构建的索引不支持动态添加、删除和更新向量。如果数据发生改变,通常需要重新构建整个索引。
- 不支持分布式存储和查询(有第三方库实现)
- 单机可能出现内存不足问题:
Traceback (most recent call last): File "*****.py", line 199, in <module> main() File "*****.py", line 93, in main train(config, train_loader, model, losses, optimizer, 0, logger) File "*****.py", line 164, in train index.add(image_embeds.view(1,-1).detach().cpu().numpy()) File "/home/ubuntu/anaconda3/envs/***/lib/python3.8/site-packages/faiss/__init__.py", line 194, in replacement_add self.add_c(n, swig_ptr(x)) File "/home/ubuntu/anaconda3/envs/***/lib/python3.8/site-packages/faiss/swigfaiss_avx2.py", line 2166, in add return _swigfaiss_avx2.IndexFlat_add(self, n, x) MemoryError: std::bad_alloc 