目录
可以访问指定路径资源的服务端
编写
引入
如果我们要访问客户端指定路径的资源,就得把请求拆分出来
- url里记录了要访问资源的路径
- 拆分的过程其实就是反序列化
介绍
那么问题就变成了 -- 如何序列化/反序列化
- 因为我们只用编写服务端(因为客户端有浏览器自动帮我们进行处理),所以只涉及请求的反序列化+响应的序列化
- 其实响应的序列化我们早就在上一个版本里做过了,我们把它再做个处理并且拆分出来
请求如何序列化(格式化数据 -> 字符串)呢?
- 把响应报头放在vector<string>里
- 响应正文单独存放在string里
- 在拼接的时候,使用某个分隔符分开他们(比如http协议里规定的\r\n,当然这个分隔符只适用于报头部分)
响应如何反序列化(字符串-> 格式化数据)呢?
- 就是把上述过程反过来
- 找到分隔符,将得到的数据赋值给结构体对应的字段
- 详细来说就是:
- 以\r\n为分隔符,找出报头的每一行,将每一行push到容器里,同时删除掉源串里的内容+"/r/n"
- 如果读到空行(内容为空)时,就已经将报头读完了
然后寻找报头里的content-length字段,找到后拿到正文长度,就可以继续把正文也拆出来了
如何得到我们的目标url呢?
- 也就是要继续细化
- url在请求行里,也就是报头的第一行=vector里的第一个元素
- 把它以空格为分隔符,拆出三大部分,即可得到纯净的url
- 我们可以手动分割
- 也可以利用ss流,它默认以空格为分隔符自动分割,只需要用变量给他接着就行(就像水倒出来,用杯子接着它哈哈哈)
得到url后,我们需要将它和我们自定义的web根目录的位置拼接起来
- 也就是在上一个版本那里介绍的那样,拼接起来得到[要访问的资源在linux中的实际路径]:
但是这里我们要增加一个特殊处理:
- 当访问根目录时,需要手动让它访问我们设定的首页文件
- 并且当访问不存在的页面时,需要手动让它访问我们设定好的错误页面
代码
#pragma once #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <cstring> #include <functional> #include "socket.hpp" #include "Serialization.hpp" static MY_SOCKET my_socket; #define buff_size 1024 * 30 #define root_path "./root_page" #define def_file "root.html" class http_server { public: http_server(const uint16_t port, const std::string &ip = "0.0.0.0") : port_(port), ip_(ip) {} ~http_server() {} void run() { init(); while (true) { uint16_t client_port; std::string client_ip; lg(DEBUG, "accepting ..."); int sockfd = my_socket.Accept(client_ip, client_port); if (sockfd == -1) { continue; } lg(INFO, "get a new link..., sockfd: %d, client ip: %s, client port: %d", sockfd, client_ip.c_str(), client_port); int ret = fork(); if (ret == 0) { my_socket.Close(); char buffer[buff_size]; std::string in_buffer; while (true) { memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); int n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); //"size"\n"a op b"\n if (n > 0) { buffer[n] = 0; lg(INFO, "get request"); in_buffer += buffer; // 连续读取 lg(INFO, "%s", in_buffer.c_str()); request req; req.deserialize(in_buffer); // 构建访问资源的路径 std::string def_page = root_path; if (req.url_ == "/") { def_page += "/"; def_page += def_file; } else { def_page += req.url_; } // 构建响应 response res; res.version_ = "HTTP/1.1"; std::string text = get_page(def_page); if (text.empty()) { res.code_ = 404; res.desc_ = "Not Found"; def_page = root_path; def_page += "/"; def_page += "404_err.html"; res.text_ = get_page(def_page); } else { res.code_ = 200; res.desc_ = "OK"; res.text_ = text; } std::string cl = "Content-Length: "; cl += std::to_string((res.text_).size()); cl += protocol_sep; (res.title_).push_back(cl); std::string content; res.serialize(content); write(sockfd, content.c_str(), content.size()); } else if (n == 0) { lg(INFO, "%s quit", client_ip.c_str()); break; } else // 读出错误 { break; } } // lg(INFO, "fork quit"); exit(0); close(sockfd); } } } private: void init() { signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN); my_socket.Socket(); my_socket.Bind(port_); my_socket.Listen(); lg(INFO, "server init done"); } std::string get_page(std::string path) { std::ifstream in(path.c_str()); if (!in.is_open()) { return ""; } std::string content, tmp; while (std::getline(in, tmp)) { content += tmp; } return content; } private: uint16_t port_; std::string ip_; };Serialization.hpp
#pragma once #include <string> #include <vector> #include <sstream> #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #define protocol_sep "\r\n" #define blank_sep ' ' class request { public: request() : type_(""), url_(""), version_(""), text_("") {} bool deserialize(std::string &content) { std::string tmp; size_t left = 0; while (true) { size_t pos = content.find(protocol_sep, left); if (pos == std::string::npos) { return false; } tmp = content.substr(left, pos - left); // 左闭右开 left = pos + 2; if (tmp.empty()) // 读到空行 { break; } else { title_.push_back(tmp); } } // 细分请求行 std::string request_line = title_[0]; std::stringstream ss(request_line); ss >> type_ >> url_ >> version_; // 如果有正文的话 std::string comp = "Content-Length: "; bool is_find = false; int size = 0; for (auto &it : title_) { size_t pos = it.find(comp); if (pos != std::string::npos) { ssize_t right = it.find(protocol_sep); std::string s_size = it.substr(pos + comp.size(), right - pos - comp.size()); size = stoi(s_size); is_find = true; break; } } if (!is_find) { // 没有Content-Length字段 content.erase(0, left + 2); } else { text_ = content.substr(left + 2, size); content.erase(0, left + 2 + size); } return true; } public: std::string type_; std::string url_; std::string version_; std::vector<std::string> title_; std::string text_; }; class response { public: response() : version_(""), code_(0), desc_(""), text_("") {} void serialize(std::string &content) { // 响应行 std::string header = version_; header += blank_sep; header += std::to_string(code_); header += blank_sep; header += desc_; header += protocol_sep; // 响应报头 std::string attribute; for (auto &it : title_) { attribute += it; attribute += protocol_sep; } content = header + attribute + protocol_sep + text_; } public: std::string version_; int code_; std::string desc_; std::vector<std::string> title_; std::string text_; };404_err.html
这是我上网随便搜的一个(毕竟咱也不是做前端的,没必要自己写)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>404-对不起!您访问的页面不存在</title> <meta charset="UTF-8" http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <style> body { margin: 0; padding: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; color: #0e356c; display: table; font-weight: 100; font-family: 'Lato'; } .container { text-align: center; display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle } .content { text-align: center; display: inline-block; } .title { font-size: 42px; margin-bottom: 40px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="content"> <div class="title">404-对不起!您访问的页面不存在</div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
示例
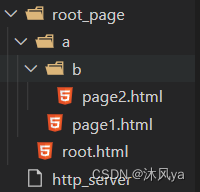
这是我们创建的多个html文件结构:
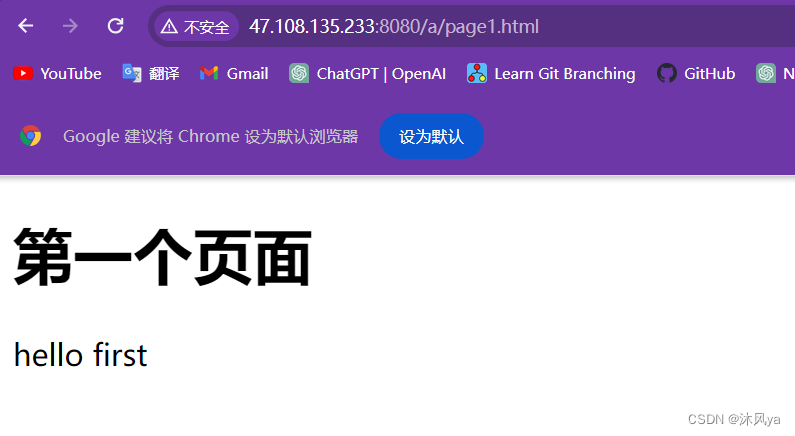
访问指定资源:
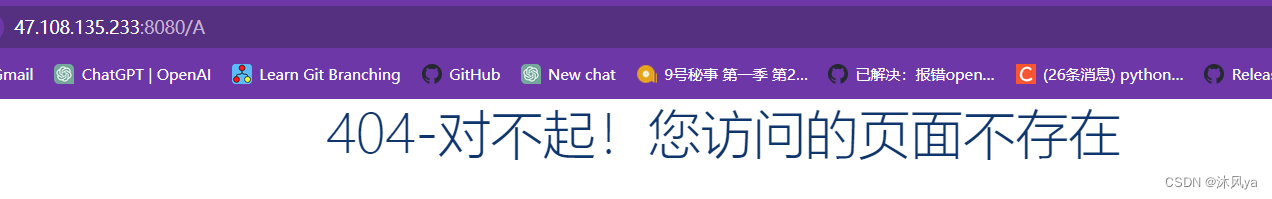
如果访问的资源不存在:
增加跳转网页功能
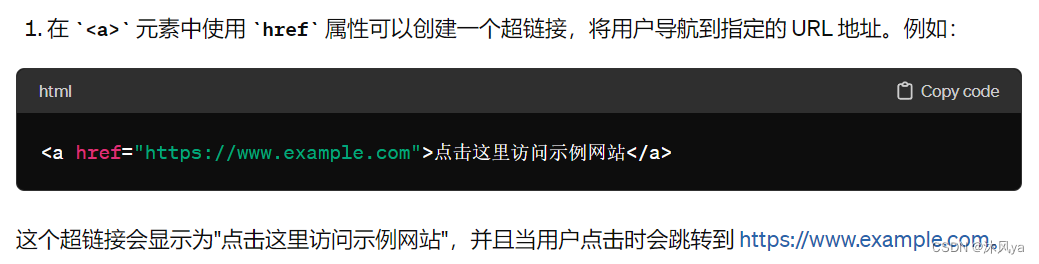
href
是 HTML 元素中常用的属性,用于指定链接的目标地址
跳转网页时不一定都发送了请求,因为浏览器会缓存一些网页
介绍
路径可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径
- 所以可以实现跳转外部/内部网页
代码
root.html
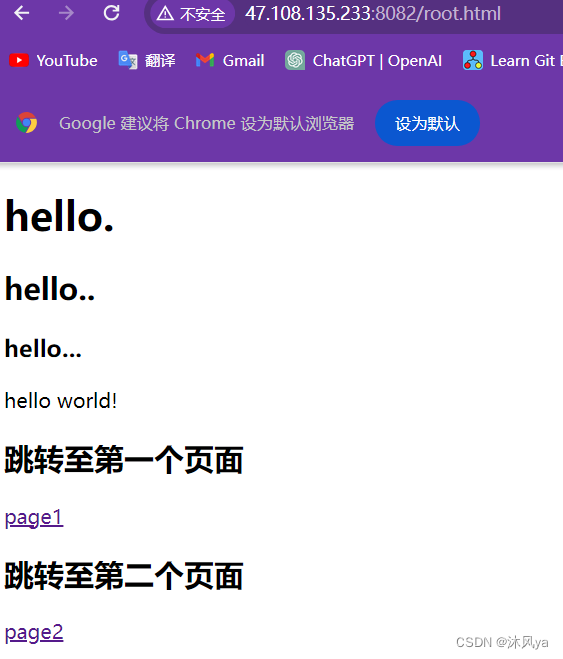
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>my title</title> </head> <body> <h1>hello.</h1> <h2>hello..</h2> <h3>hello...</h3> <p>hello world!</p> <h2>跳转至第一个页面</h2> <p><a href="a/page1.html">page1</a></p> <h2>跳转至第二个页面</h2> <p><a href="a/b/page2.html">page2</a></p> </body> </html>page1.html
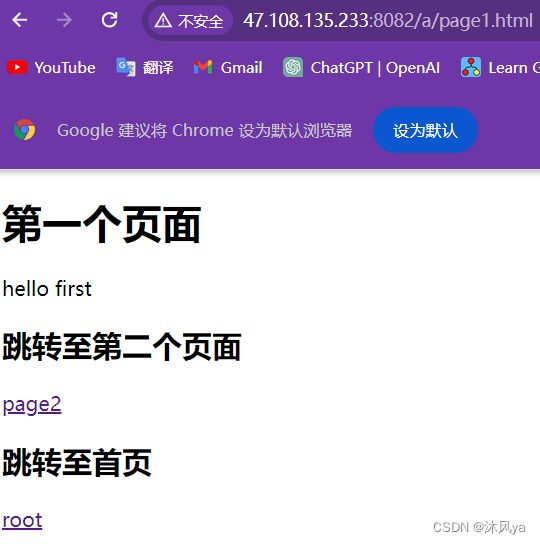
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>my title</title> </head> <body> <h1>第一个页面</h1> <p>hello first</p> <h2>跳转至第二个页面</h2> <p><a href="b/page2.html">page2</a></p> <h2>跳转至首页</h2> <p><a href="../root.html">root</a></p> </body> </html>page2.html
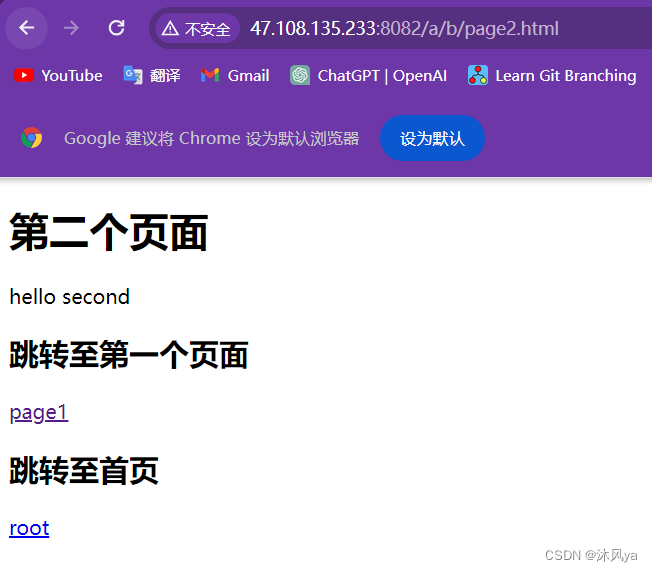
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>my title</title> </head> <body> <h1>第二个页面</h1> <p>hello second</p> <h2>跳转至第一个页面</h2> <p><a href="../page1.html">page1</a></p> <h2>跳转至首页</h2> <p><a href="../../root.html">root</a></p> </body> </html>
示例
当我们首先访问page2:
点击跳转首页后:
点击跳转page1后:
添加重定向功能
引入
我们在上一篇博客中介绍过重定向的概念 -- 域名介绍,url的介绍+原理+特殊字符的处理,网络行为,http协议请求/响应的格式+结构,状态码介绍,临时/永久重定向,http报头常见字段,fiddler-CSDN博客
介绍
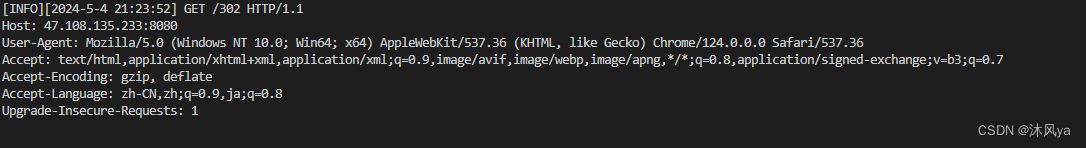
我们这里假定当客户端访问/302时,就触发重定向功能
- 也就是让响应的状态码为302
- 浏览器会帮我们根据http协议 -- 当状态码为302时,自动跳转到location字段定义的资源(这里我们设置为百度主页,都行的啦)
- 因为只是一个测试嘛,起到一个看看重定向效果的作用
代码
只需要修改动态构建响应部分即可:
void run() { init(); while (true) { uint16_t client_port; std::string client_ip; lg(DEBUG, "accepting ..."); int sockfd = my_socket.Accept(client_ip, client_port); if (sockfd == -1) { continue; } lg(INFO, "get a new link..., sockfd: %d, client ip: %s, client port: %d", sockfd, client_ip.c_str(), client_port); int ret = fork(); if (ret == 0) { my_socket.Close(); char buffer[buff_size]; std::string in_buffer; while (true) { memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); int n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); //"size"\n"a op b"\n if (n > 0) { bool code_302 = false; buffer[n] = 0; lg(INFO, "get request"); in_buffer += buffer; // 连续读取 lg(INFO, "%s", in_buffer.c_str()); request req; req.deserialize(in_buffer); // 构建访问资源的路径 std::string def_page = root_path; if (req.url_ == "/") { def_page += "/"; def_page += def_file; } else if (req.url_ == "/302") { code_302 = true; } else { def_page += req.url_; } // 构建响应 response res; res.version_ = "HTTP/1.1"; if (code_302) { res.code_ = 302; res.desc_ = "Found"; std::string cl = "Location: "; cl += "https://www.baidu.com"; cl += protocol_sep; (res.title_).push_back(cl); } else { std::string text = get_page(def_page); if (text.empty()) { res.code_ = 404; res.desc_ = "Not Found"; def_page = root_path; def_page += "/"; def_page += "404_err.html"; res.text_ = get_page(def_page); } else { res.code_ = 200; res.desc_ = "OK"; res.text_ = text; } std::string cl = "Content-Length: "; cl += std::to_string((res.text_).size()); cl += protocol_sep; (res.title_).push_back(cl); } std::string content; res.serialize(content); write(sockfd, content.c_str(), content.size()); } else if (n == 0) { lg(INFO, "%s quit", client_ip.c_str()); break; } else // 读出错误 { break; } } // lg(INFO, "fork quit"); exit(0); close(sockfd); } } }
示例
服务端收到的请求:
成功跳转到我们设定好的百度主页
- 有时候可能会一直转圈圈,多切换下网络
添加显示图片功能
引入
网页一般都会有图片
- 图片也属于网络资源,也需要浏览器向服务器请求这个资源
- 所以图片资源也会放在web根目录下
这也就意味着:
- 当我们请求一个页面后,浏览器不仅需要请求网页,还需要根据页面标签定义的图片资源挨个请求
这也就是为什么新版本的http要支持长连接:
- 如果还采用短连接,一个连接=一个资源,那万一网页有几百张图片资源,那不得连接死
介绍
插入图片资源的html语法: -- HTML 图像
图片资源其实就是二进制文件,它需要被上层以某种格式解释,才能呈现出我们想要看到的样子
- 所以就需要添加conten-type字段,来指定该资源的类型
- 我们之前都没有使用过这个字段,所以他默认以html格式解释
- 如果是图片的话,就得是image/jpeg / image/png
但是,那么多资源,如何识别哪个资源是那个类型呢?
- 我们就需要继续细分url了
- url不是记录了客户端要访问的资源路径吗,就肯定会带上资源的文件名
- 如果文件名带有.jpg / .png后缀,则为图片资源
- 如果带有.html后缀,则是我们普通的网页资源
- 如果是其他的,就默认以html格式解释(这里就简单一点处理啦)
那么,有了后缀,我们还需要将后缀与对应的conten-type的填充值相关联
- 所以我们需要定义一个键值对容器
既然图片是二进制,那如果还使用[读取文本文件的一行一行读]的方式就不行了
- 需要增加一个读取二进制的函数,用来区分两者
代码
除了增加了读取图片资源的功能,我还把代码结构修改了很多
http_server.hpp
#pragma once #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <cstring> #include <functional> #include <unordered_map> #include "socket.hpp" #include "Serialization.hpp" static MY_SOCKET my_socket; #define buff_size 1024 * 30 class http_server { public: http_server(const uint16_t port, const std::string &ip = "0.0.0.0") : port_(port), ip_(ip) { content_type_[".html"] = "text/html"; content_type_[".png"] = "image/png"; content_type_[".jpg"] = "image/jpeg"; content_type_[".jpeg"] = "image/jpeg"; } ~http_server() {} void run() { init(); while (true) { uint16_t client_port; std::string client_ip; lg(DEBUG, "accepting ..."); int sockfd = my_socket.Accept(client_ip, client_port); if (sockfd == -1) { continue; } lg(INFO, "get a new link..., sockfd: %d, client ip: %s, client port: %d", sockfd, client_ip.c_str(), client_port); int ret = fork(); if (ret == 0) { my_socket.Close(); char buffer[buff_size]; std::string in_buffer; while (true) { memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); int n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); //"size"\n"a op b"\n if (n > 0) { buffer[n] = 0; in_buffer += buffer; // 连续读取 lg(INFO, "get request: \n%s", in_buffer.c_str()); // 构建请求 request req; req.deserialize(in_buffer); //lg(DEBUG, "path: %s ,url: %s ", (req.path_).c_str(), (req.url_).c_str()); // 构建响应 response res; handle_response(res, req); // 响应序列化 std::string content; res.serialize(content); write(sockfd, content.c_str(), content.size()); } else if (n == 0) { lg(INFO, "%s quit", client_ip.c_str()); break; } else // 读出错误 { break; } } exit(0); close(sockfd); } } } private: void init() { signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN); my_socket.Socket(); my_socket.Bind(port_); my_socket.Listen(); lg(INFO, "server init done"); } void handle_response(response &res, request &req) { int code = req.code_; std::string path = req.path_; std::string content_type_data = content_type_[req.suffix_]; //lg(DEBUG, "content_type_data: %s", content_type_data.c_str()); res.version_ = "HTTP/1.1"; if (code == 302) { res.code_ = 302; res.desc_ = "Found"; std::string cl = "Location: "; cl += "https://www.qq.com"; (res.title_).push_back(cl); return ; } if (code == 404) { res.code_ = 404; res.desc_ = "Not Found"; } else { res.code_ = 200; res.desc_ = "OK"; } // 将读取网页和图片资源的方式分开 if (req.suffix_ == ".html") { res.text_ = get_page(path); //lg(DEBUG, "text: %s", (res.text_).c_str()); } else { res.text_ = b_get_page(path); } // 构建响应报头 std::string cl = "Content-Length: "; cl += std::to_string((res.text_).size()); //lg(DEBUG, "text_size: %d", (res.text_).size()); (res.title_).push_back(cl); cl = "Content-Type: "; cl += content_type_data; (res.title_).push_back(cl); } private: uint16_t port_; std::string ip_; std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> content_type_; };Serialization.hpp
#pragma once #include <string> #include <vector> #include <sstream> #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #define protocol_sep "\r\n" #define blank_sep ' ' #define root_path "./root_page" #define def_file "root.html" std::string get_page(std::string path) { std::string content, tmp; std::ifstream in(path.c_str()); if (!in.is_open()) { return ""; } while (std::getline(in, tmp)) { content += tmp; } in.close(); // printf("content : %s", content.c_str()); return content; } std::string b_get_page(std::string path) { std::ifstream in(path.c_str(), std::ios_base::binary); if (!in.is_open()) { return ""; } in.seekg(0, std::ios_base::end); auto len = in.tellg(); in.seekg(0, std::ios_base::beg); std::string content; content.resize(len); in.read((char *)content.c_str(), content.size()); in.close(); return content; } class request { public: request() : type_(""), url_(""), version_(""), text_(""), path_(""), code_(0), suffix_("") {} bool deserialize(std::string &content) { std::string tmp; size_t left = 0; while (true) { size_t pos = content.find(protocol_sep, left); if (pos == std::string::npos) { return false; } tmp = content.substr(left, pos - left); // 左闭右开 left = pos + 2; if (tmp.empty()) // 读到空行 { break; } else { title_.push_back(tmp); } } // 判断是否有正文 std::string comp = "Content-Length: "; bool is_find = false; int size = 0; for (auto &it : title_) { size_t pos = it.find(comp); if (pos != std::string::npos) { ssize_t right = it.find(protocol_sep); std::string s_size = it.substr(pos + comp.size(), right - pos - comp.size()); size = stoi(s_size); is_find = true; break; } } if (!is_find) { // 没有Content-Length字段 content.erase(0, left + 2); } else { text_ = content.substr(left + 2, size); content.erase(0, left + 2 + size); } handle_path(); return true; } private: void handle_path() // 构建访问资源的路径 { // 细分请求行 std::string request_line = title_[0]; std::stringstream ss(request_line); ss >> type_ >> url_ >> version_; // 构建路径 path_ = root_path; if (url_ == "/") { path_ += "/"; path_ += def_file; } else if (url_ == "/302") { code_ = 302; // 这里设置为重定向到百度页面,所以不能走本地读取 return; } else { path_ += url_; } // 判断该资源是否存在 if (get_page(path_).empty()) { code_ = 404; // 需要告诉响应,这里发生了404错误 path_ = root_path; path_ += "/"; path_ += "404_err.html"; } // 拿到资源后缀 size_t pos = path_.rfind("."); if (pos == std::string::npos) { suffix_ = ".html"; } else { suffix_ = path_.substr(pos); } } public: std::string type_; std::string url_; std::string path_; int code_; std::string suffix_; std::string version_; std::vector<std::string> title_; std::string text_; }; class response { public: response() : version_(""), code_(0), desc_(""), text_("") {} void serialize(std::string &content) { // 响应行 std::string header = version_; header += blank_sep; header += std::to_string(code_); header += blank_sep; header += desc_; header += protocol_sep; // 响应报头 std::string attribute; for (auto &it : title_) { attribute += it; attribute += protocol_sep; } content = header + attribute + protocol_sep + text_; } public: std::string version_; int code_; std::string desc_; std::vector<std::string> title_; std::string text_; };root_page.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>my title</title> </head> <body> <h1>hello.</h1> <h2>hello..</h2> <h3>hello...</h3> <p>hello world!</p> <form action="a/page1.html" method="get"> name:<input type="text" name="name"><br> password:<input type="password" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" name="submit"> </form> <img src="1.jpeg" alt="猫猫" width="500" height="400"> <h2>跳转至第一个页面</h2> <p><a href="a/page1.html">page1</a></p> <h2>跳转至第二个页面</h2> <p><a href="a/b/page2.html">page2</a></p> </body> </html>
示例
当我们在首页放上我们的图片资源时
- 访问首页后,浏览器就会根据页面上的html标签继续申请其他资源
- 这是网页的样式(可以看到图片成功被加载出来了):
修改为多线程版(短连接)
介绍
服务器收到一个连接后,就创建一个线程去处理请求
- 并且添加了重连功能
注意:
- 我们这里是短连接版本,一次连接=处理一次请求
- 但即使是短连接,也得保证读取到的数据是一份完整的请求
- 所以我在线程外部定义了一个缓冲区,用于保存处理过程中剩下的数据(因为它有可能是其他连接的一部分)
- 而线程内部在反序列化时,将完整请求从缓冲区中剥离
代码
#pragma once #include <signal.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <cstring> #include <functional> #include <pthread.h> #include <unordered_map> #include "socket.hpp" #include "Serialization.hpp" static MY_SOCKET my_socket; #define buff_size 1024 * 30 class http_server; struct thread_data { int sockfd_; std::string ip_; std::string &in_buffer_; http_server *this_; }; class http_server { public: http_server(const uint16_t port, const std::string &ip = "0.0.0.0") : port_(port), ip_(ip) { content_type_[".html"] = "text/html"; content_type_[".png"] = "image/png"; content_type_[".jpg"] = "image/jpeg"; content_type_[".jpeg"] = "image/jpeg"; } ~http_server() {} void run() { init(); while (true) { uint16_t client_port; std::string client_ip; // 一个线程处理一次请求(短连接) pthread_t pid; std::string in_buffer; int sockfd = 0; int count = 5; do { lg(DEBUG, "accepting ..."); sockfd = my_socket.Accept(client_ip, client_port); if (sockfd != -1 || --count == 0) { break; } } while (true); if (sockfd == -1) { lg(ERROR, "accepting error"); } lg(INFO, "get a new link..., sockfd: %d, client ip: %s, client port: %d", sockfd, client_ip.c_str(), client_port); thread_data *td = new thread_data{sockfd, client_ip, in_buffer, this}; lg(DEBUG, "create pthread"); pthread_create(&pid, nullptr, entry, reinterpret_cast<void *>(td)); // 一个进程服务一个客户端 // lg(DEBUG, "accepting ..."); // int sockfd = my_socket.Accept(client_ip, client_port); // if (sockfd == -1) // { // continue; // } // lg(INFO, "get a new link..., sockfd: %d, client ip: %s, client port: %d", sockfd, client_ip.c_str(), client_port); // int ret = fork(); // if (ret == 0) // { // my_socket.Close(); // char buffer[buff_size]; // std::string in_buffer; // while (true) // { // memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); // int n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); //"size"\n"a op b"\n // if (n > 0) // { // buffer[n] = 0; // in_buffer += buffer; // 连续读取 // lg(INFO, "get request: \n%s", in_buffer.c_str()); // // 构建请求 // request req; // req.deserialize(in_buffer); // // lg(DEBUG, "path: %s ,url: %s ", (req.path_).c_str(), (req.url_).c_str()); // // 构建响应 // response res; // handle_response(res, req); // // 响应序列化 // std::string content; // res.serialize(content); // write(sockfd, content.c_str(), content.size()); // } // else if (n == 0) // { // lg(INFO, "%s quit", client_ip.c_str()); // break; // } // else // 读出错误 // { // break; // } // } // exit(0); // close(sockfd); // } } } private: void init() { signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN); my_socket.Socket(); my_socket.Bind(port_); my_socket.Listen(); lg(INFO, "server init done"); } void handle_response(response &res, request &req) { int code = req.code_; std::string path = req.path_; std::string content_type_data = content_type_[req.suffix_]; // lg(DEBUG, "content_type_data: %s", content_type_data.c_str()); res.version_ = "HTTP/1.1"; if (code == 302) { res.code_ = 302; res.desc_ = "Found"; std::string cl = "Location: "; cl += "https://www.qq.com"; (res.title_).push_back(cl); return; } if (code == 404) { res.code_ = 404; res.desc_ = "Not Found"; } else { res.code_ = 200; res.desc_ = "OK"; } // 将读取网页和图片资源的方式分开 if (req.suffix_ == ".html") { res.text_ = get_page(path); // lg(DEBUG, "text: %s", (res.text_).c_str()); } else { res.text_ = b_get_page(path); } // 构建响应报头 std::string cl = "Content-Length: "; cl += std::to_string((res.text_).size()); // lg(DEBUG, "text_size: %d", (res.text_).size()); (res.title_).push_back(cl); cl = "Content-Type: "; cl += content_type_data; (res.title_).push_back(cl); } static void *entry(void *args) { pthread_detach(pthread_self()); thread_data *td = reinterpret_cast<thread_data *>(args); int sockfd = td->sockfd_; std::string ip = td->ip_; std::string in_buffer = td->in_buffer_; http_server *it = td->this_; // 读取请求 char buffer[buff_size]; bool flag = true; request req; while (true) // 虽说是短连接,但也得确保读出来的内容是一个完整的请求 { memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer)); int n = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)); if (n > 0) { buffer[n] = 0; in_buffer += buffer; // 连续读取 lg(INFO, "get request: \n%s", in_buffer.c_str()); // 构建请求 flag = req.deserialize(in_buffer); if (flag == false) { continue; } else { break; } } else if (n == 0) { lg(INFO, "%s quit", ip.c_str()); return nullptr; } else { lg(ERROR, "%s read error", ip.c_str()); return nullptr; } } // lg(DEBUG, "path: %s ,url: %s ", (req.path_).c_str(), (req.url_).c_str()); // 构建响应 response res; it->handle_response(res, req); // 响应序列化 std::string content; res.serialize(content); write(sockfd, content.c_str(), content.size()); // 销毁资源 delete td; close(sockfd); return nullptr; } private: uint16_t port_; std::string ip_; std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> content_type_; };